Table Layout
Header Style
The Header Style popup allows you to change the background, text, and border colors for column headers. For example, this Tabular View uses a blue background and red border:
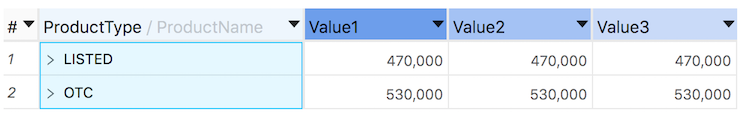
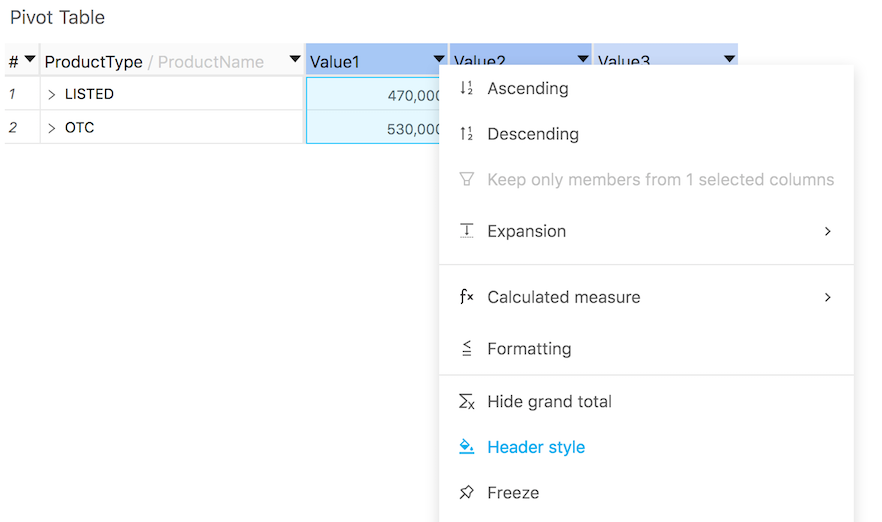
Right click on a column header in Tabular View or Pivot Table to access the Header Style context Menu:
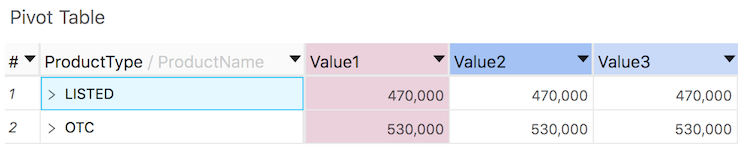
You can combine header styles with Formatting to improve readability, as in the pink column below:
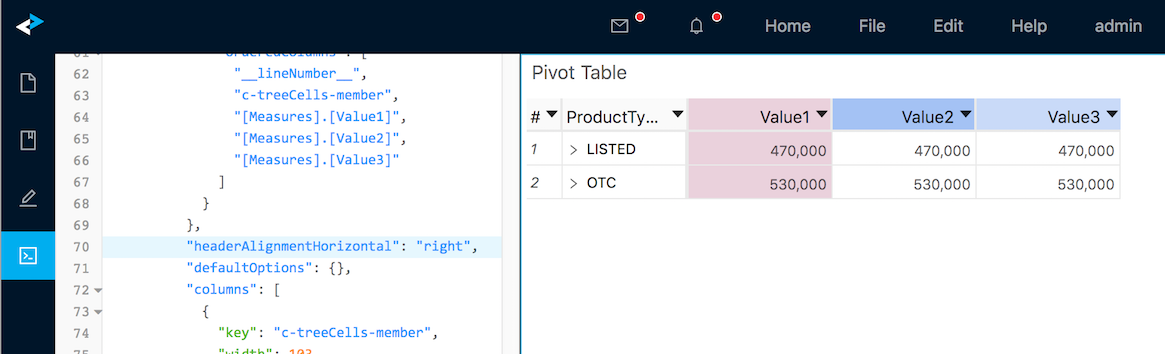
- You can format the alignment of headers and cells in the State Editor. Headers can be vertically or horizontally aligned by the
headerAlignmentHorizontalandheaderAlignmentVerticalattributes. To align horizontally you can useleft,rightorcenter. To align vertically you can usetop,bottomormiddle. - Similarly cells can be aligned based on numeric or nonnumeric type with
cellAlignmentNumericHorizontal,cellAlignmentNonNumericHorizontal,cellAlignmentNumericVerticalandcellAlignmentNonNumericVerticalattributes.
Freeze Columns
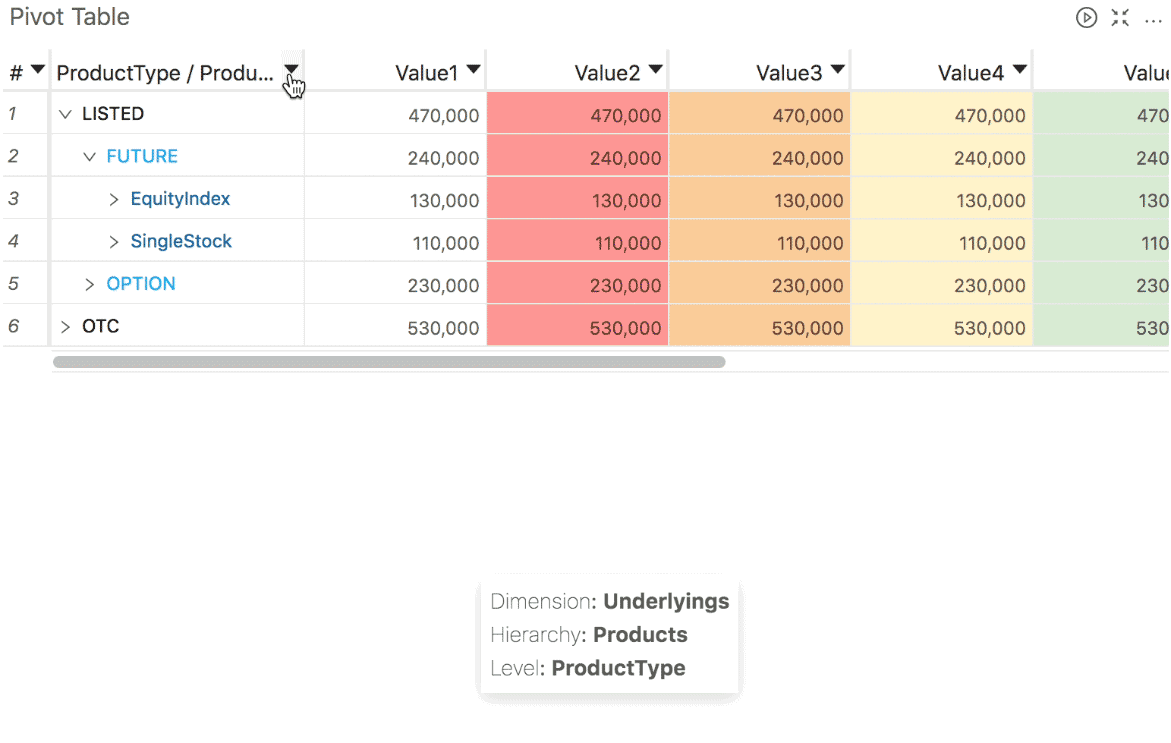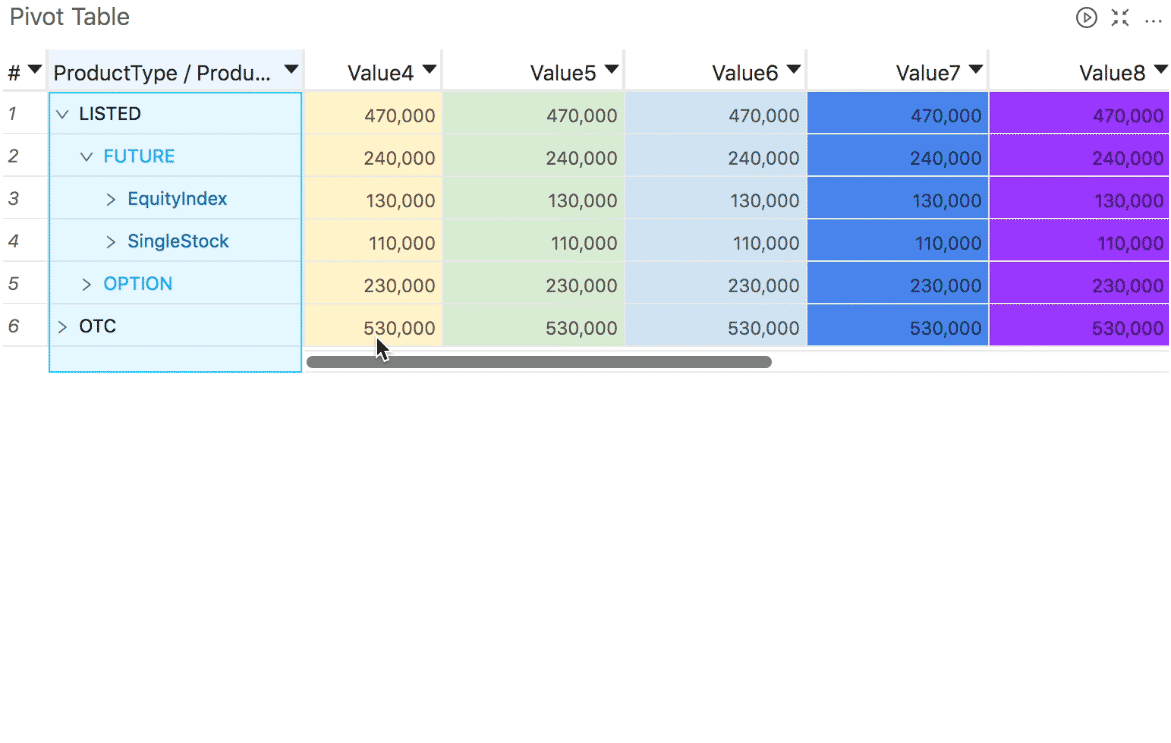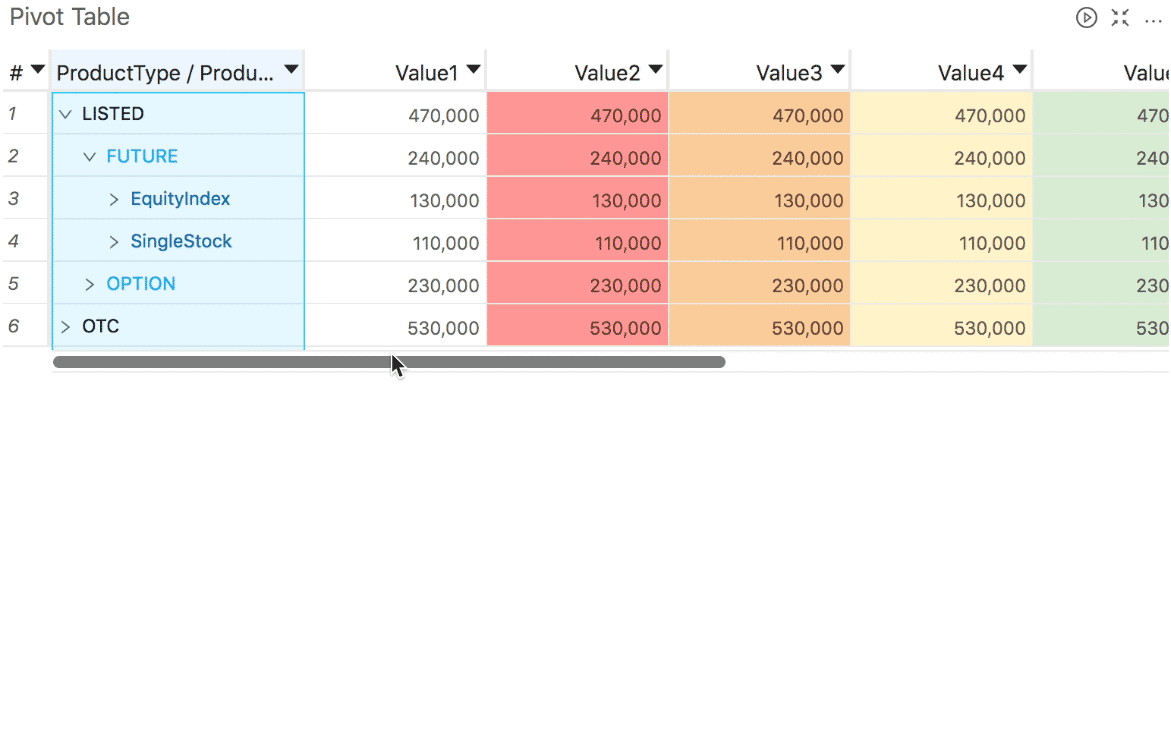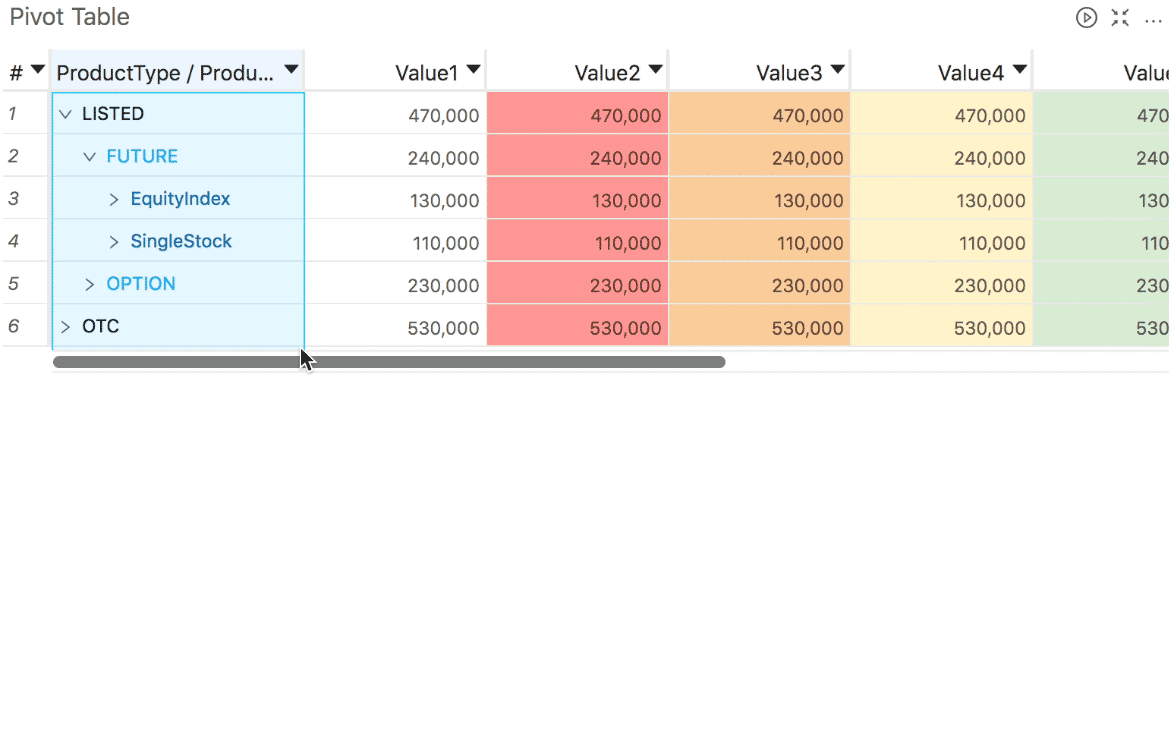
To lock a column when scrolling data in a widget, right click and select "Freeze".
Move Columns
Columns can be manually reordered. To do this, select the columns to move by dragging over their headers. Once selected, columns can be dragged and dropped where desired.
Remove Column
Right click on a column header and select Remove to delete it.
To restore a column you have previously deleted, you must select the measure or dimension again. (See Pivot Table and Tabular View.)
Rename Column
By default, the column header displays the measure, formula, dimension name, or the value from the cube. Double click the header to edit.
By accessing the MDX behind the widget, it is possible to rename measures, aggregation levels, create named combinations, and apply virtually any transformation to the data. Read more about editing the MDX using the Mdx Editor.
Change width
To manually change the column width, drag its border.
To automatically resize a column to its widest displayed cell, double-click on its right border. If the automatically resized column is part of a column selection, all columns from that selection will also be resized. So it is possible to automatically resize all columns by selecting the whole table and double-clicking on any column.
The automatic resizing only takes into account visible cells and ignores the headers. So it is possible to resize a whole table in three quick steps: first select all columns, then double-click on the right border of any header to automatically resize the column widths, then double-click on the header lower bar to automatically resize the header heights.
Advanced users can predefine the column width of a particular column in the State Editor.
Text wrapping
Text wrapping in column headers with long captions will break the text by words initially, and then by letters inside a word if necessary.
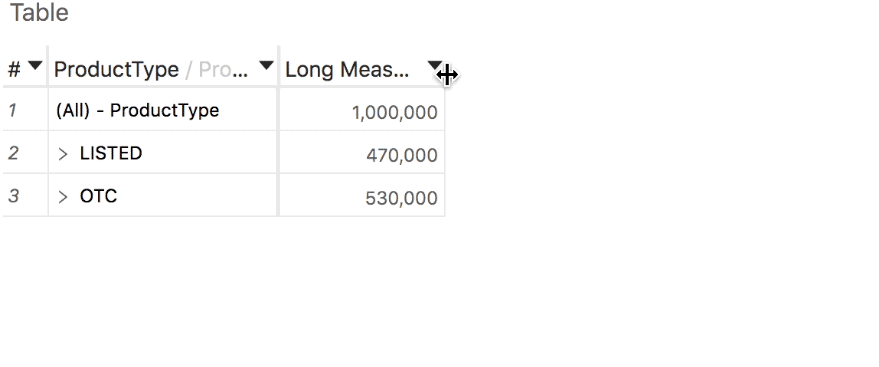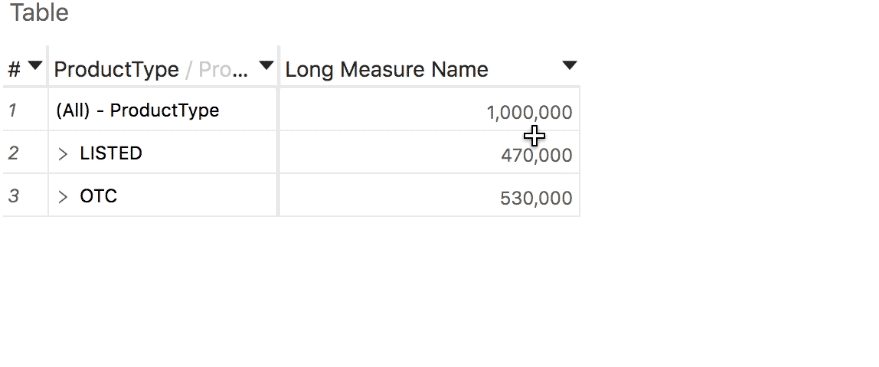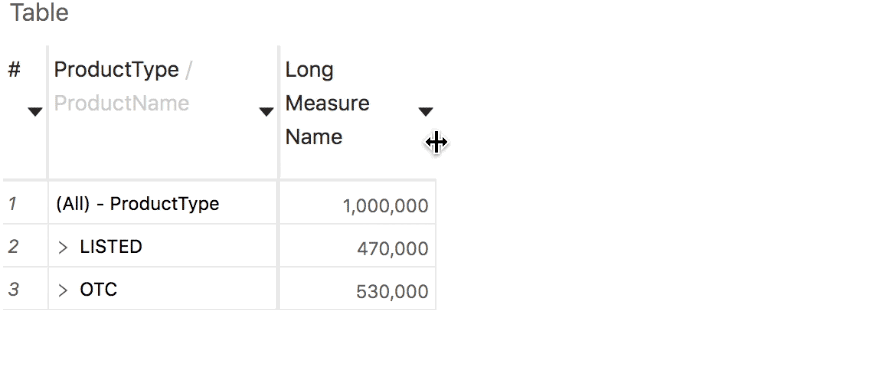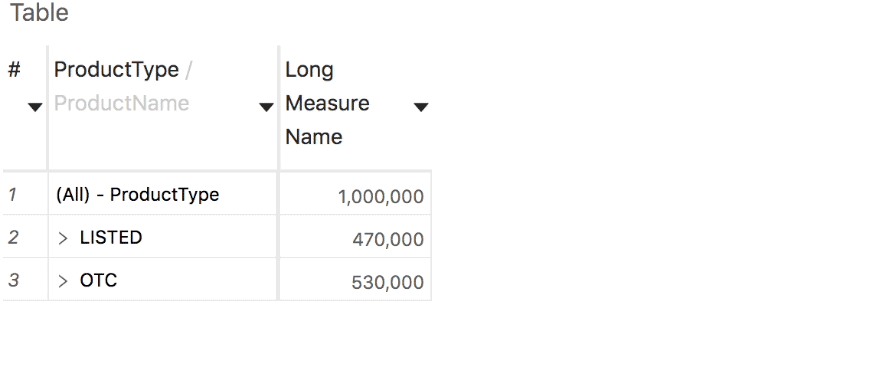
Selection statistics
From ActiveUI 4.2.0 onwards, it is possible to select cell ranges in a Pivot Table and a Tabular View to display simple metrics for the selected cells (Sum, Count, Minimum, Maximum, Average, and Count numbers) beneath the table:
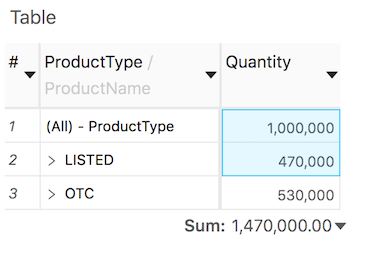
Advanced users can disable/enable Statistics by setting the "statisticsShown" property to false/true in the table’s State.
Be aware that Statistics only performs simple computations based on the selected cells. Please do not attempt to use it to sum up "apples and oranges".
Sparklines
A group of numeric columns can be replaced by sparklines – small column graphs without axes:
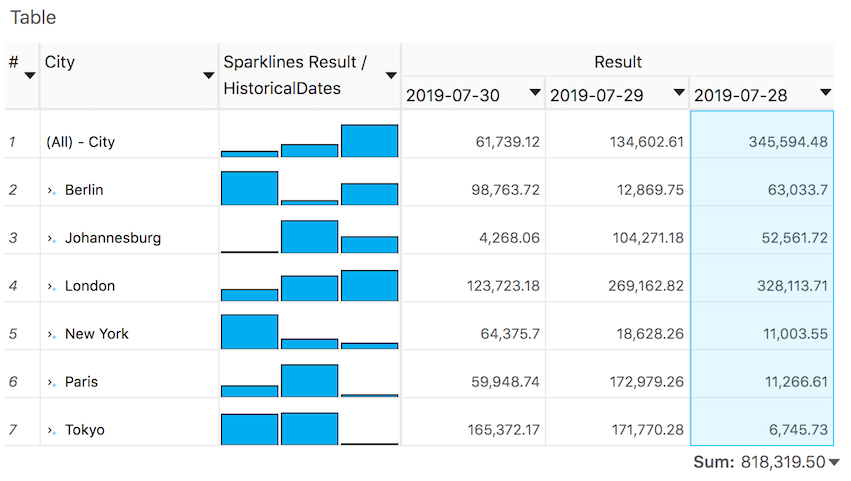
To replace columns with sparklines, select these columns and then choose Create Sparklines from the selection's context menu.
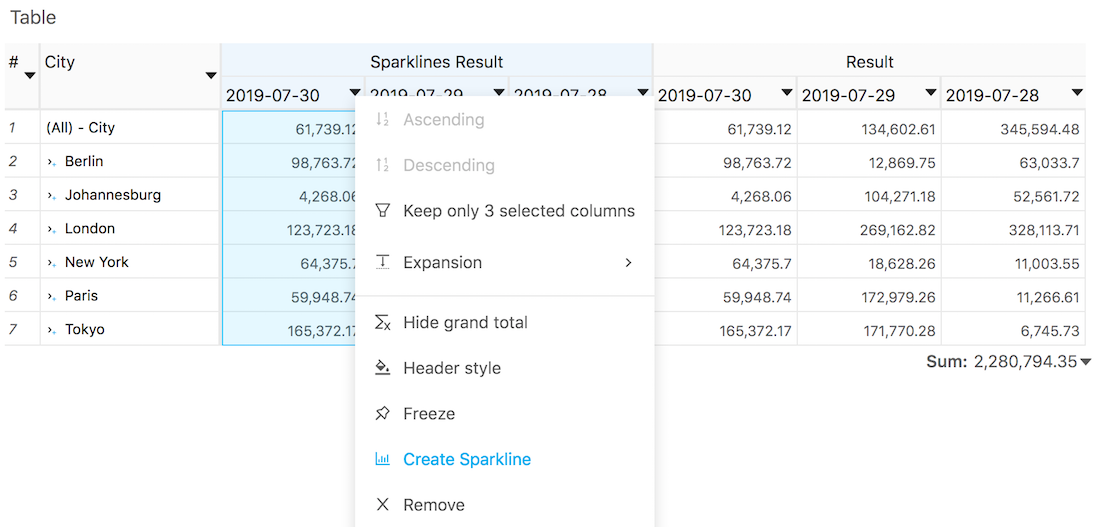
To turn sparklines back into separate columns, select Ungroup from the column's context menu.
Show and hide totals
- The Tabular View is a flat representation of your data and therefore doesn't show any total.
- The Pivot Table shows totals by default but you can hide some or all of them, if you need to.
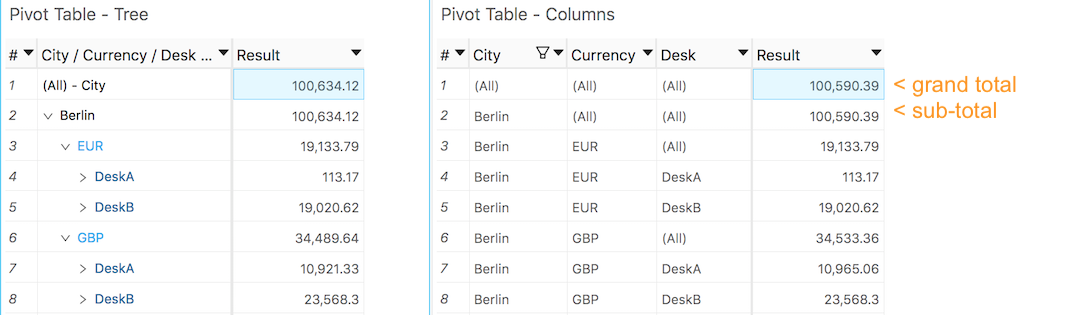
Sub-totals
There are 2 main ways of showing and hiding sub-totals:
The Content Editor gives you control over the subtotals and totals that will be requested from ActivePivot.
By default, you can always drag hierarchies (as opposed to levels). This way, you will obtain all the totals. Then you can easily select which to hide and which to show.
You can use the Hide sub-total and Show sub-total context menu options, as shown below (these options will also work, assuming that the corresponding subtotals exist, as described in the first bullet-point).
If the pivot table is "displayed as tree", you will find the Hide sub-total option on subtotal rows, and the Show sub-total option on rows corresponding to the first member of a level where subtotals are hidden (where you would expect this subtotal to be shown).
Advanced users may control the subtotals using the
mdx.hiddenSubtotalscontext value.
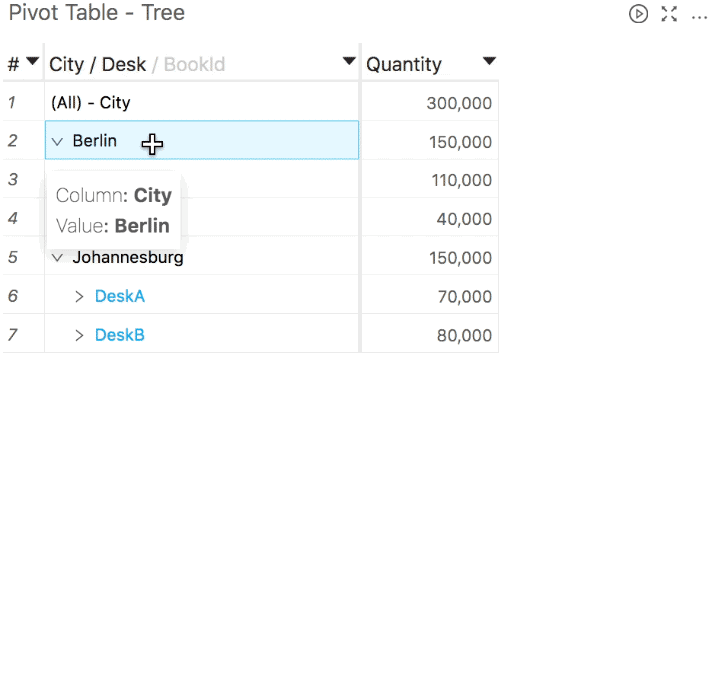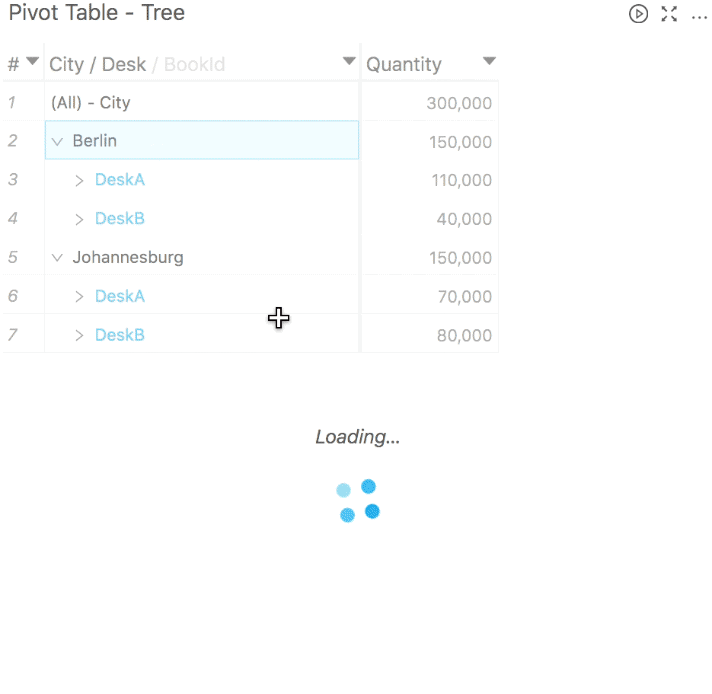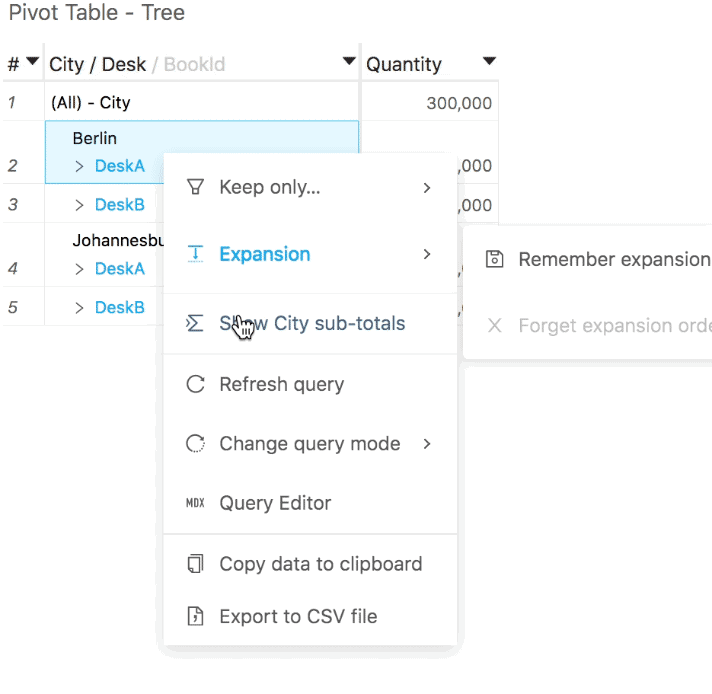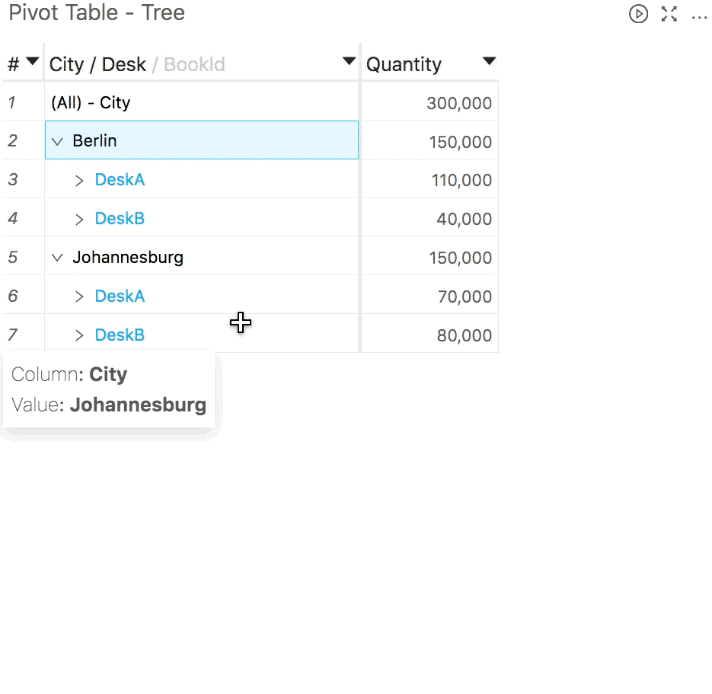
If it is "displayed as columns", you can click anywhere within a column to show or hide its subtotals.
Grand totals
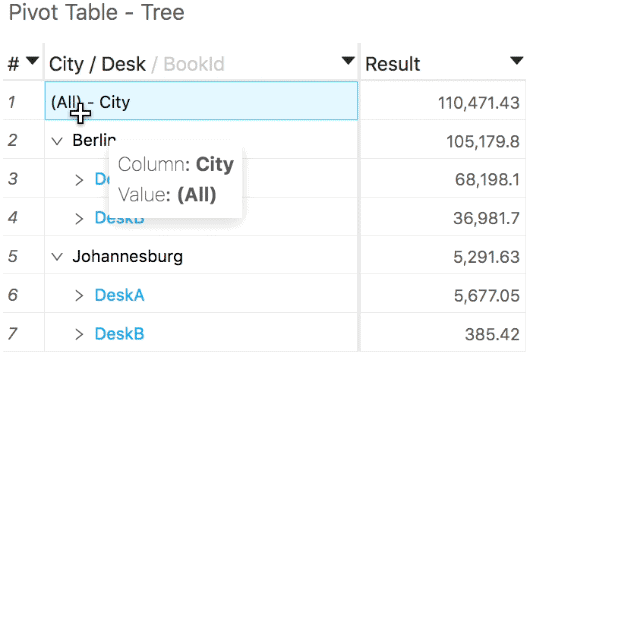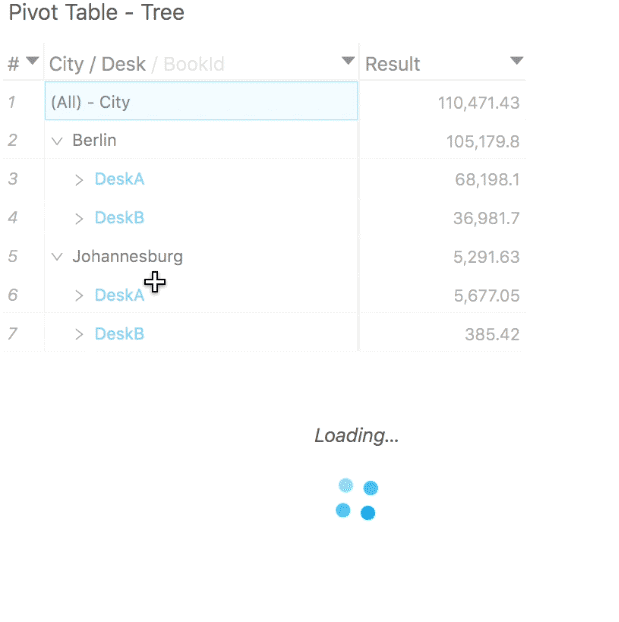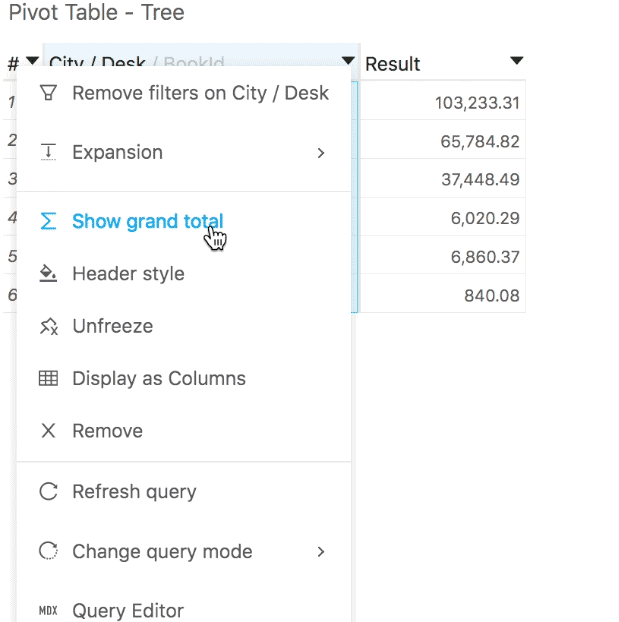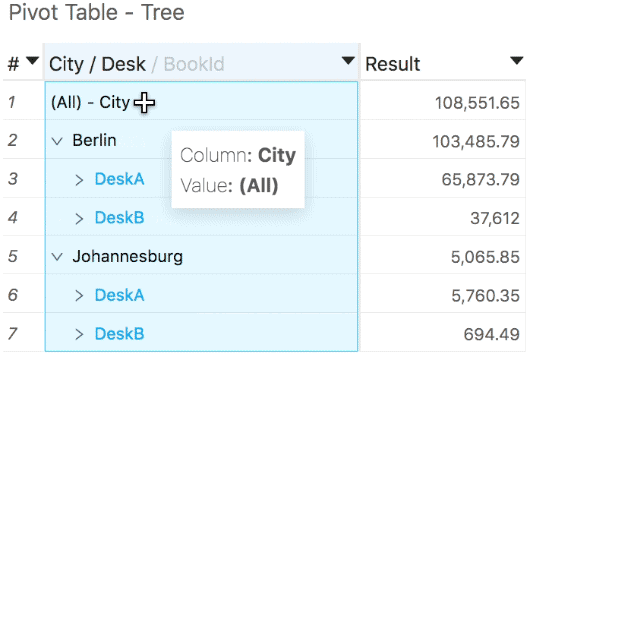
You can similarly hide or show the grand total of a pivot table:
- This grand total will be returned by ActivePivot if all child levels and their totals are requested (please refer to the previous tip).
- It can be hidden using the Hide grand total context menu option. This option is available on the table header and on the grand total row. When the grand total is hidden, you can get it back by using the Show grand total option, available on the table header.
Advanced users may control the grand totals using the
mdx.hiddenGrandTotalscontext value.