KPI
What is a KPI?
A KPI defines:
- a measure that needs to be tracked,
- a critical interval made up of one or more static or dynamic thresholds that the will trigger alerts when the measure crosses them.
This will create a KPI status that will return -1, 0 or 1, respectively for "Breach", "Success" and "Warning". Each of those values are interpreted as icons by the Pivot Table and Tabular View widgets.
KPIs are part of the cube's definition and are independant of the ActiveMonitor component.
Each KPI defines:
- KPI Value, which returns the actual value of the associated measure.
- KPI Goal, which returns the value of the benchmark.
- KPI Status, which returns the state of a KPI.
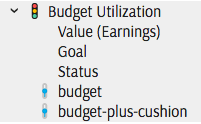
Parameters linked to a KPI are also available for selection (one of them will match the Goal):
Create new KPI
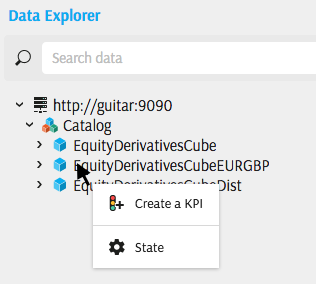
A new KPI must be created using the following steps:
Use the cube's context menu in the Data Explorer and select Create a KPI:
Use the column's context menu in a Pivot Table or Tabular View and select Watch.
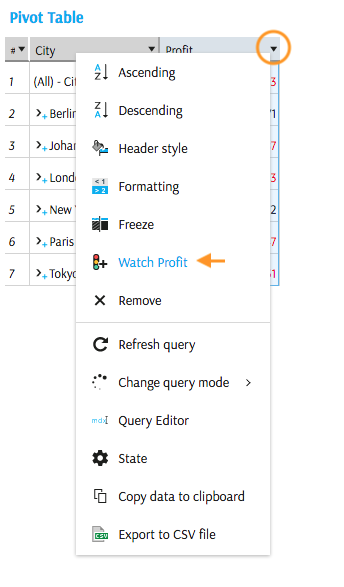
The KPI Editor pops up:
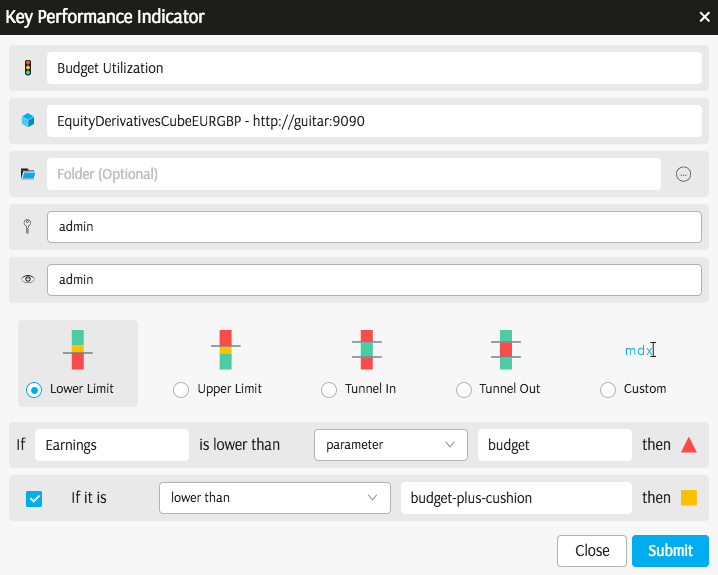
In the KPI Editor:
- Type the required KPI Name. When giving the KPI a name, take into consideration that "KPI Name Status" and "KPI Name Goal" will be appearing in table headers, unless you rename them.
- Select/see which cube schema the KPI belongs to.
- Select a folder.
- Owner. Select from the list of users or user groups configured in your organization. Owners are allowed to edit the KPI.
- Reader. Select from the list of users or user groups configured in your organization. Readers are allowed to view the KPI.
- Select the critical interval setting (see below).
- Select the measure to be monitored.
You may publish a custom calculation into the cube using Calculation Editor and create a KPI to watch it. Follow this link to see an Example.
Critical interval
The lower part of the KPI editor facilitates the ation of a critical interval. When a KPI Value is inside the critical interval, the status is "red".
In the KPI Editor you may select:
- Lower limit - KPI status is red if the value is below the critical value
- Upper Limit - KPI status is red if the value is above the critical value
- Tunnel In - KPI status is red if the value is below or above the critical values for the Lower Limit or Upper Limit respectively.
- Tunnel Out - KPI status is red if the value is not higher and not lower than the critical values (which means it is equal to one of the critical value, or somewhere in between them)
- Custom - MDX is used to define critical intervals.
Advanced users are able to switch to Custom mode and view the MDX generated by different types of critical intervals. Follow this link to see an Example.
Critical values or boundaries of the critical interval may be set as:
- measures (floating critical values)
- parameters (collections of static values for different aggregation levels)
- values (single static values)
You may also define a warning interval, corresponding to "amber" status of a KPI.
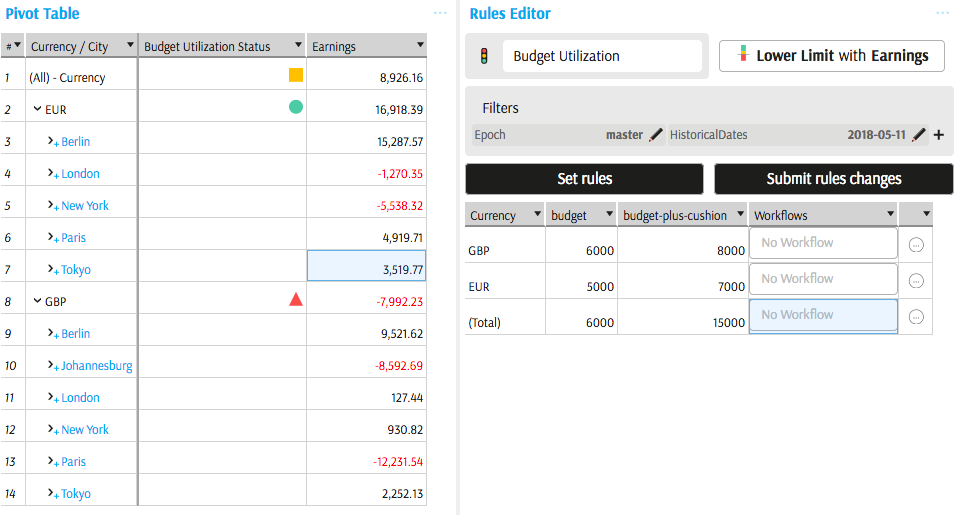
In the Budget Utilization example above, the KPI status is red when Earnings are below the critical values mapped to a parameter called budget. The KPI status is amber when Earnings are below another parameter, called budget-plus-cushion. These parameters are part of the Rules.
Remove KPI
To be able to delete a KPI, you must be one of the Owners of that KPI. To actually delete the KPI, right-click on it in the Data Explorer.
Deleting a KPI removes it from the cube schema. If your organization does not have a backup or an audit mechanism for the cube schema, then the KPI cannot be recovered. Please consult your product development team to learn more about your implementation.
Edit KPI
If you are one of the KPI's Owners, you can right-click a KPI and edit its properties, as described above.
Analyse KPI in a view
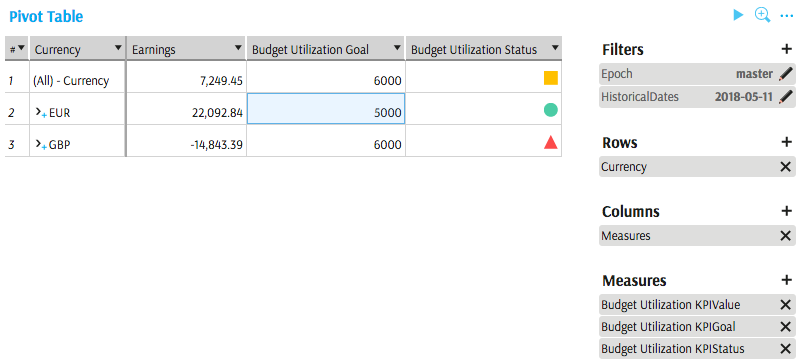
KPI Value, Goal, Status and parameters are available for selection in all types of data presentation widgets.
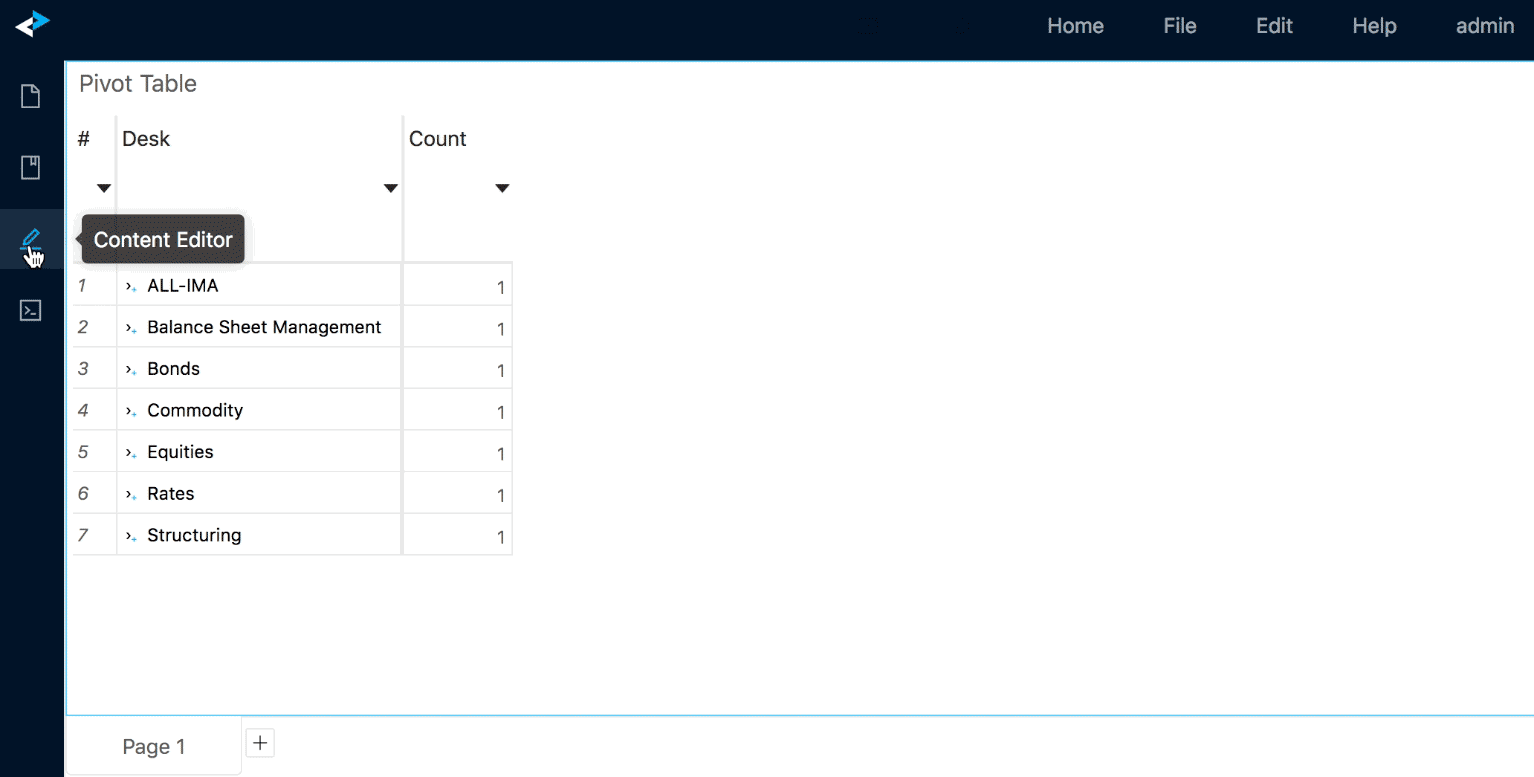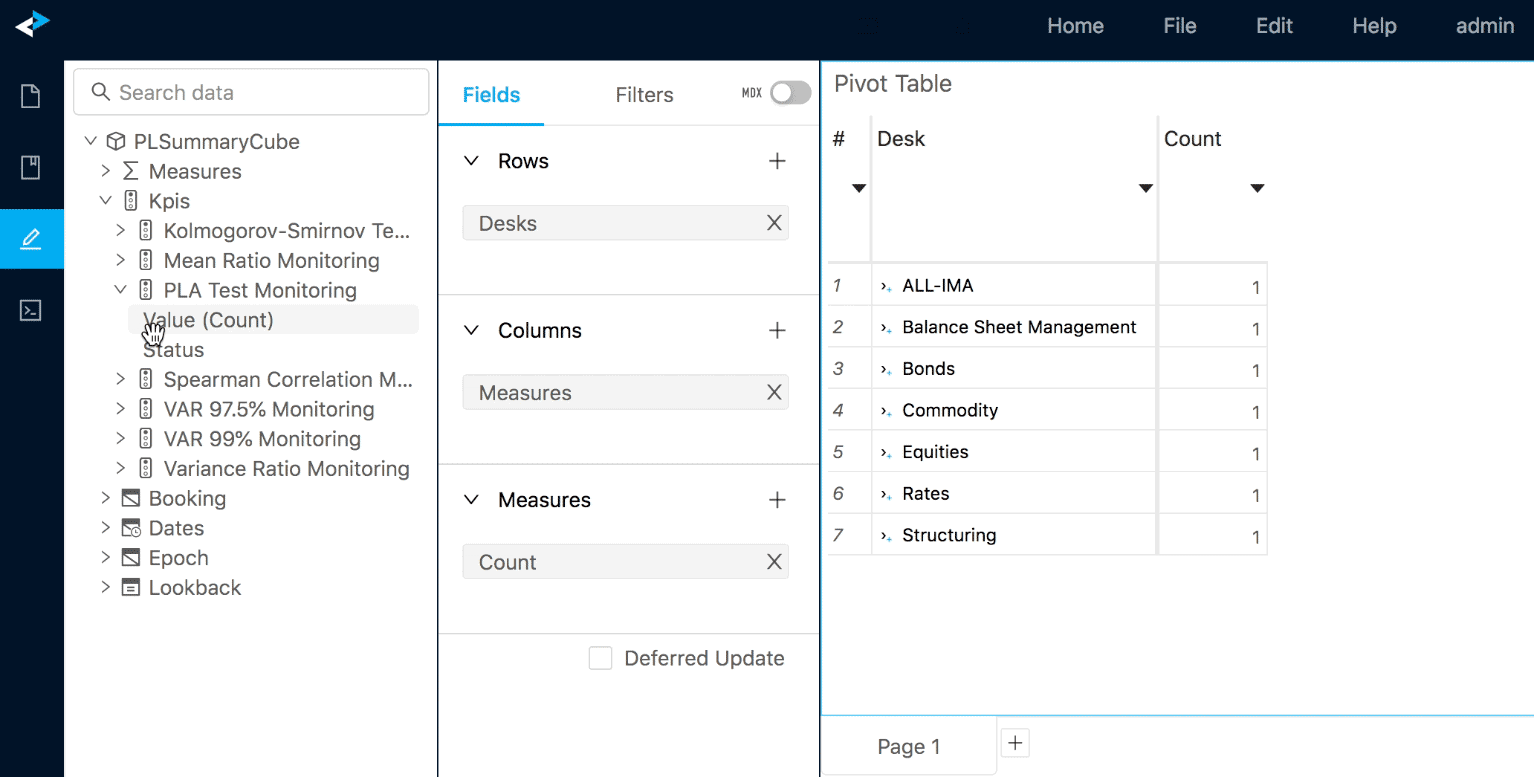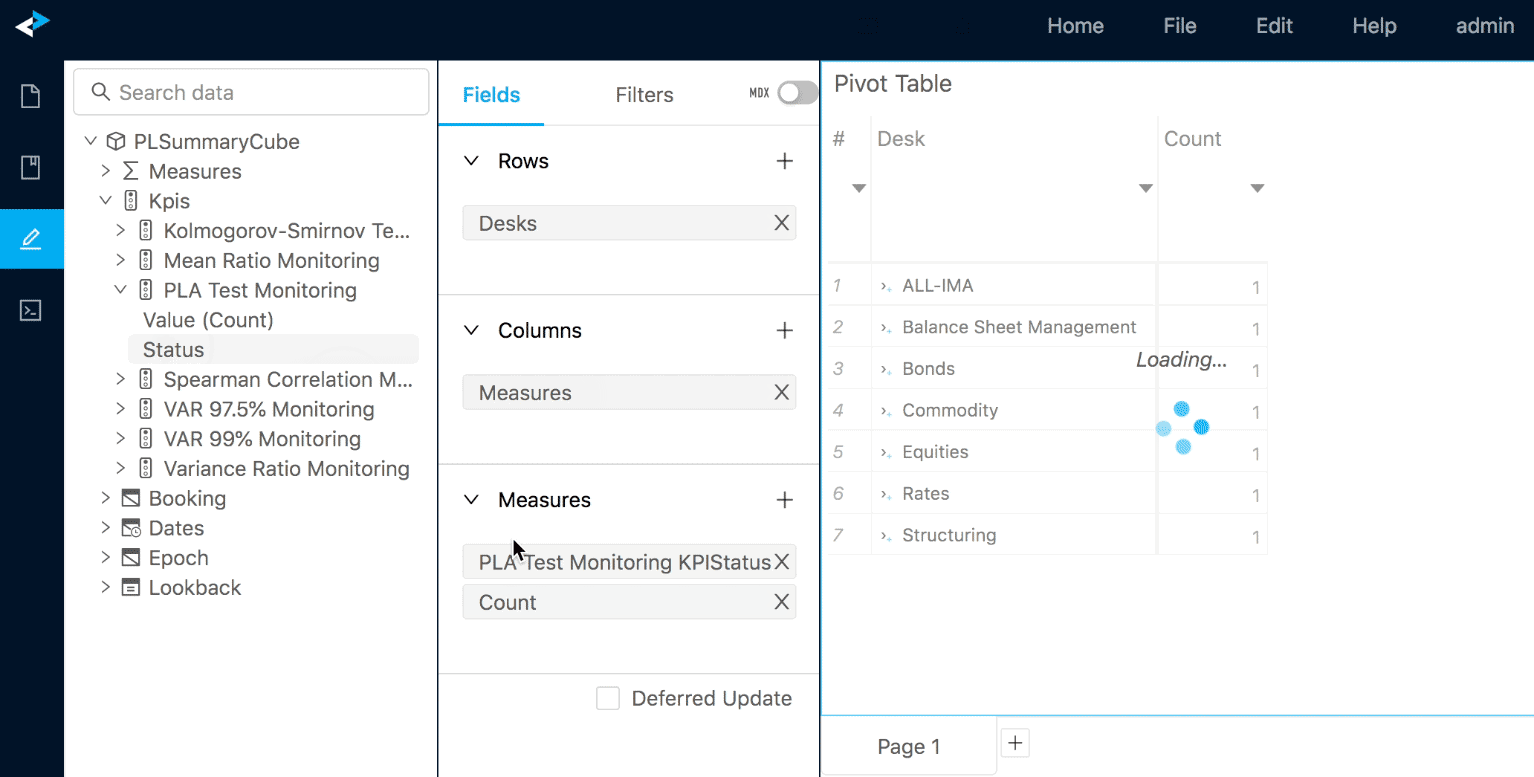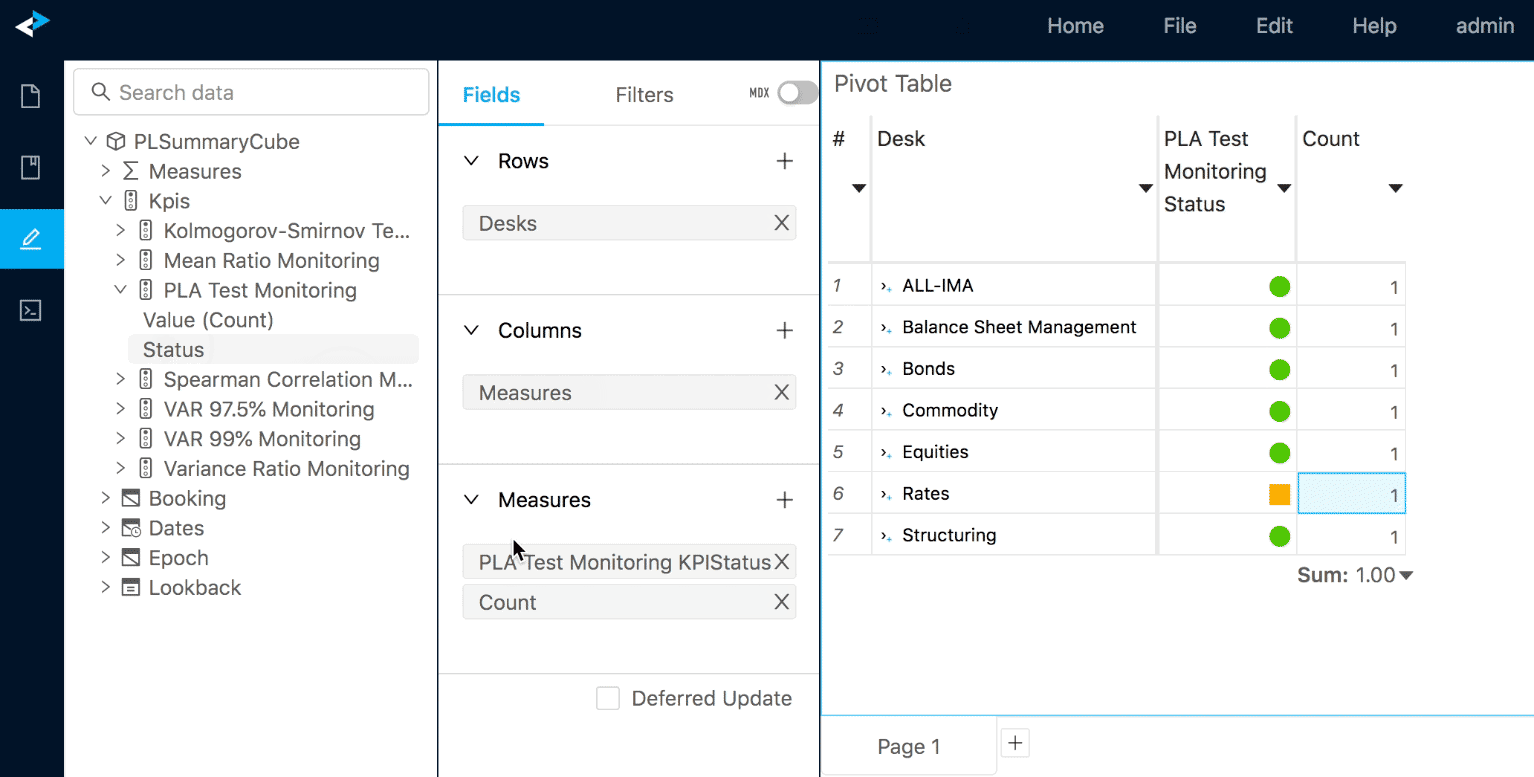
If set, Rules may limit the scope for KPI Status evaluations. In the example shown below, Rules are set for Total and for individual currencies. No Rules are set for combinations of cities and currencies, hence the status is not evaluated: