Caching side stores
The Atoti Market Risk schema contains a number of side stores. These stores are not part of the star-schema — they are not joined to any of the base stores — but they contain reference data. During a calculation data is retrieved from these stores by way of get-by-key, list, or distinct queries. In the course of a complex calculation, such as PnL Explain, there may be many thousands of these queries.
With an in-memory Atoti application, the datastore is highly optimized to handle these operations and, even with high volumes, they are executed quickly. However, in an Atoti application using DirectQuery, each of these queries must be executed on the external database. This may mean many thousands of database queries over a network, which will drastically slow any user workflows.
Atoti Market Risk includes two solutions to this problem: full table caching and the DirectQuery Local Cache.
Full table caching
Overview
With this approach, at startup, a side store is copied in its entirety from the external database to an in-memory datastore. From there, the data can be queried with the full performance of an Atoti Server in-memory application. This is the default approach in Atoti Market Risk, used for all side stores.
Configured stores
Specifically, the following stores will be cached:
- SpotMarketData
- CurveMarketData
- SurfaceMarketData
- CubeMarketData
- FxRateMarketData
- Scenarios
- CorrelationMarketData
- DividendMarketData
- SplitRatioMarketData
- MarketShifts
- DynamicTenors
- DynamicMaturities
- DynamicMoneyness
- SensiLadders
- CubeLevelAdjustments (if using Sign-Off)
Quickstart
If you are using Atoti Market Risk out-of-the box, without customization, you don’t need to make any changes to use this feature. Simply follow the instructions to enable DirectQuery and the configured stores listed in the preceding section will be automatically cached at startup.
Detailed setup
If you have made changes to Atoti Market Risk or are only using specific components, this section describes how caching is configured and the classes you need to ensure are present in your application.
The ISideStoresToClone interface is used to declare stores to be cached. Beans of this type are autowired to DirectQueryActivePivotConfig where they
are configured for caching.
Atoti Market Risk has configuration classes that define these beans for you. Make sure they are imported in your project for the configured stores to be cached.
| Store | Configuration class | Module | Imported by |
|---|---|---|---|
| SpotMarketData | DQCommonStoreConfig | mr-common-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| CurveMarketData | DQCommonStoreConfig | mr-common-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| SurfaceMarketData | DQCommonStoreConfig | mr-common-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| CubeMarketData | DQCommonStoreConfig | mr-common-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| FxRateMarketData | DQCommonStoreConfig | mr-common-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| Scenarios | DQStandardStoreConfig | mr-common-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| CorrelationMarketData | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| DividendMarketData | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| SplitRatioMarketData | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| MarketShifts | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| DynamicTenors | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| DynamicMaturities | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| DynamicMoneyness | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| SensiLadders | DQSensiStoreConfig | mr-sensi-config | SensiCompleteConfig |
| CubeLevelAdjustments | SignOffTaskConfig | mr-application | MarketRiskConfig |
At startup, Atoti Market Risk will create the appropriate DirectQuery schema and copy all rows from the underlying database table to the cache store. Once this is complete, you can query the cache stores just as you would query any of these stores when running Atoti Market Risk in-memory. Indeed, the cache stores are created with the same name as the store would have in an in-memory application, so you should not need to make any changes to existing post-processors.
note
- This feature relies on the
Migrator, a component used by Atoti Market Risk to create the Atoti Server schema. Ensure you are using the Migrator in your project to use this feature. - The
DirectQueryActivePivotConfigclass in themr-directquerymodule contains the Migrator configuration. Ensure this class is imported in your project for the cache to work. This class is imported byMRDirectQueryConfigwhich is itself imported byMarketRiskConfigin themr-applicationmodule.
Customizations
Caching a new store
To create and cache a new side store, you must add the store to the datastore description and define a source configuration. The source configuration is used to load data into the store.
With that in place, simply expose an ISideStoresToClone bean providing the name of your store to be cached.
@Bean
public ISideStoresToClone customStoresToClone() {
return collection -> {
collection.add("MyCustomTable");
};
}
note
- This feature relies on the
Migrator, a component used by Atoti Market Risk to create the Atoti Server schema. Ensure you are using the Migrator in your project to use this feature. - The
DirectQueryActivePivotConfigclass in themr-directquerymodule contains the Migrator configuration. Ensure this class is imported in your project for the cache to work. This class is imported byMRDirectQueryConfigwhich is itself imported byMarketRiskConfigin themr-applicationmodule.
warning
Only side stores can be cached in-memory.
You can’t cache referenced stores as the reference would be between in-memory and remote tables, which is not supported.
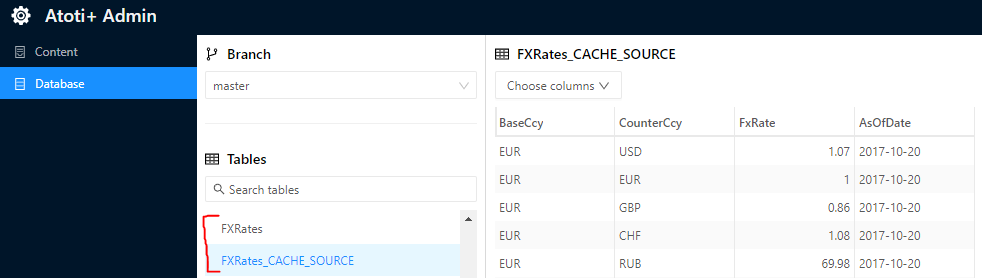
Validate the setup
You can validate that a cache is configured correctly by taking a look in Atoti Admin UI. You should see one store with the “_CACHE_SOURCE” suffix — this is the table in the database. The in-memory table is the one without the suffix.
In the screenshot you can see the Table “FXRates” as both an in-memory store (named “FXRates”) and as a remote DirectQuery database table (named “FXRates_CACHE_SOURCE”). Both of these stores contain the same data.
DirectQuery Local Cache
Overview
Full table caching provides excellent performance in terms of retrieving data. However, it may result in high memory consumption. Some side stores contain a significant volume of data and, particularly when the dataset spans a long time, it may be prohibitive to store this entirely in memory.
The DirectQuery Local Cache is a solution for these cases. Instead of caching the entire table, the DirectQuery Local Cache only stores partitions of the underlying table. These partitions are loaded when required by a particular query and held in memory until the cache exceeds a specified size. This cache is built into Atoti Server, and Atoti Market Risk is configured to use this cache for specific side stores.
See the Atoti Server DirectQuery Local Cache documentation to understand how the cache works, and for details on how to use it in an Atoti application. For this guide, we will assume you have read this documentation.
Configured stores
The following stores are currently configured to work with the DirectQuery Local Cache:
- SpotMarketData
- CurveMarketData
- SurfaceMarketData
- CubeMarketData
- FxRateMarketData
- CorrelationMarketData
- DividendMarketData
- SplitRatioMarketData
- MarketShifts
Quickstart
If you are using Atoti Market Risk out-of-the box, without customization, this feature is enabled by setting the following property:
mr.enable.preview.directquery-cache=true
With this property set, the configured stores listed in the preceding sections will be configured to use the DirectQuery Local Cache. All other side stores will continue to use full table caching. Atoti Market Risk post-processors that retrieve data from these stores are configured to populate the caches as required.
Cache partitioning
Each cache stores a number of cache partitions. Each partition is a subset of the overall table. Partitions are loaded into the cache based on the requirements of a query.
For the market data stores — SpotMarketData, CurveMarketData, SurfaceMarketData, CubeMarketData, FxRateMarketData, CorrelationMarketData and DividendMarketData — the caches are partitioned by AsOfDate and MarketDataSet. The SplitRatioMarketData store is partitioned by AsOfDate only.
For the MarketShifts store, the cache is partitioned by AsOfDate and ScenarioSet.
Cache capacity
Each cache is created with a cache capacity, which determines the maximum number of rows or partitions to keep in the cache. You can configure the cache capacity by exposing a supplier bean for the relevant cache.
@Configuration
public class CacheCapacityConfig {
// Set the capacity of the SpotMarketData store
@Bean
public SpotMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier spotCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the CurveMarketData store
@Bean
public CurveMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier curvCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the SurfaceMarketData store
@Bean
public SurfaceMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier surfaceCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the CubeMarketData store
@Bean
public CubeMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier cubeCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the FxRateMarketData store
@Bean
public FxRateMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier fxRateCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the CorrelationMarketData store
@Bean
public CorrelationMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier correlationCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the DividendMarketData store
@Bean
public DividendMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier dividendCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the SplitRatioMarketData store
@Bean
public SplitRatioMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier splitRatioCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
// Set the capacity of the MarketShifts store
@Bean
public MarketShiftDirectQueryCacheConfig.CacheCapacitySupplier marketShiftCapacity() {
return () -> CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(5);
}
}
Detailed setup
If you have made changes to Atoti Market Risk or are only using specific components, this section describes how caching is configured and the classes you need to ensure are present in your application.
Cache descriptions
For a store to be cached, a cache description must be created at startup and fed into the Atoti application. Atoti Market Risk includes cache descriptions for each of the configured stores, contained in a Spring configuration class and exposed as a bean.
| Store | Configuration class | Module | Imported by |
|---|---|---|---|
| SpotMarketData | SpotMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | market-data-config (Atoti Market Data) | AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is imported by MarketRiskConfig |
| CurveMarketData | CurveMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | market-data-config (Atoti Market Data) | AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is imported by MarketRiskConfig |
| SurfaceMarketData | SurfaceMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | market-data-config (Atoti Market Data) | AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is imported by MarketRiskConfig |
| CubeMarketData | CubeMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | market-data-config (Atoti Market Data) | AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is imported by MarketRiskConfig |
| FxRateMarketData | FxRateMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | market-data-config (Atoti Market Data) | AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is imported by MarketRiskConfig |
| CorrelationMarketData | CorrelationMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | mr-sensi-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| DividendMarketData | DividendMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | mr-sensi-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| SplitRatioMarketData | SplitRatioMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig | mr-sensi-config | MarketRiskConfig |
| MarketShifts | MarketShiftDirectQueryCacheConfig | mr-sensi-config | MarketRiskConfig |
note
If you aren’t using all of these stores in your project, you may remove the corresponding imports from MarketRiskConfig.
The DirectQueryActivePivotConfig class in the mr-directquery module collects these cache description beans and feeds them into the application configuration.
Make sure this class is imported in your project for the cache to work. This class is imported by MRDirectQueryConfig which is itself imported by
MarketRiskConfig in the mr-application module.
IDatabaseCacheManager
You add data to the cache by defining a DatabaseCachePrefetcher in post-processors that query the cache. To create this prefetcher, the post-processor requires an instance of the
IDatabaseCacheManager.
The cache manager is exposed as a bean by the DirectQueryActivePivotConfig class in the mr-directquery module, after it has created
the application. Make sure this class is imported in your project to have access to the cache manager. This class is imported by MRDirectQueryConfig, which is
itself imported by MarketRiskConfig in the mr-application module.
The cache manager is injected into relevant post-processors by the RiskPostProcessorInjector configuration class in the mr-application module. Make sure
this class is imported in your project for the injection to take place. This class is imported by MarketRiskConfig in the mr-application module. If you are
not using the RiskPostProcessorInjector you will need to inject the cache manager yourself:
Registry.getExtendedPlugin(IPostProcessor.class)
.values()
.stream()
.filter(ppFactory -> IMRDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(ppFactory.getImplementationClass()))
.forEach(ppFactory -> ppFactory.getStateTransfer().inject(IDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.PROPERTY_NAME, databaseCacheManager));
note
- Atoti Market Risk uses the Atoti Market Data module for the market data stores and post-processors. The
IDatabaseCacheManageris injected into Atoti Market Data post-processors by thecom.activeviam.marketdata.config.directquery.DatabaseCacheManagerInjectionConfigconfiguration class. Ensure this is imported in your project. - If you are using the out-of-the-box Atoti Market Risk project, it is imported in
AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is itself imported byMarketRiskConfig.
Market shift post-processor configuration
There are a number of post-processors in Atoti Market Risk that retrieve data from the MarketShifts store. Each post-processor creates a DatabaseCachePrefetcher
which dictates how the cache will be populated, considering the partitioning of the cache. To ensure a common configuration for each of these post-processors
the application injects the cache configuration into them directly.
The configuration is contained in the MarketShiftDirectQueryCachePostProcessorConfig class in the mr-sensi-config module. Make sure this class is imported
in your project to create the MarketShift cache configuration beans. This class is imported by MarketRiskConfig in the mr-application module.
note
The cache configuration is injected into relevant post-processors by the RiskPostProcessorInjector configuration class in the mr-application module. Ensure
this class is imported in your project for the injection to take place. This class is imported by MarketRiskConfig in the mr-application module. If you are
not using the RiskPostProcessorInjector, you need to inject the cache manager yourself:
Registry.getExtendedPlugin(IPostProcessor.class)
.values()
.stream()
.filter(ppFactory -> IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(ppFactory.getImplementationClass()))
.forEach(ppFactory -> ppFactory.getStateTransfer().inject(IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.PROPERTY_NAME, marketShiftConfiguration));
Customizations
Cache partition customizations
As described in Cache partitioning, market data caches are partitioned by AsOfDate and MarketDataSet. It is not currently possible to change this partitioning.
The MarketShift cache is partitioned by AsOfDate and ScenarioSet. To change this you need to:
- Provide a new cache definition with your required partitioning. Be sure to remove
MarketShiftDirectQueryCacheConfigfromMarketRiskConfigas this provides the default cache definition. - Provide a new
IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.CacheConfigurationwith a location converter to work with your partitioning. This configuration will be injected to relevant post-processors if you follow the steps described in Market shift post-processor configuration. Be sure to removeMarketShiftDirectQueryCachePostProcessorConfigfromMarketRiskConfigas this provides the default cache configuration.
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryDatabase
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryCacheEnabled
public class CustomMarketShiftCacheConfig {
// Provide a custom cache description for the MarketShifts store.
@Bean
public SingleTableCacheDescription marketShiftsStoreCacheDescription() {
return SingleTableCacheDescription.builder()
.tableName(StoreConstants.MARKET_SHIFT_STORE_NAME)
.cachePartitioningFields(List.of("AsOfDate", "Custom")) // Insert custom partitioning fields here.
.capacity(CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(6))
.build();
}
// Provide a custom cache configuration for post-processors using the MarketShifts store.
@Bean
public IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.CacheConfiguration marketShiftCacheConfiguration() {
return new IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor.CacheConfiguration(
StoreConstants.MARKET_SHIFT_STORE_NAME,
new BestEffortLocationToCachePartitionConverter(List.of(
new LevelIdentifier("Date", "Dates", "AsOfDate"),
new LevelIdentifier("Custom", "Custom", "Custom"))));
}
}
Custom post-processors
If you have a custom post-processor that will be executing queries on the configured stores, you need to set these up to use the cache.
This involves adding a DatabaseCachePrefetcher in your post-processor. See the Atoti Server documentation Pre-fetch cache partition in post-processors
.
Market data caches
The following stores are defined in Atoti Market Data:
- SpotMarketData
- CurveMarketData
- SurfaceMarketData
- CubeMarketData
- FxRateMarketData
The following stores are defined in Atoti Market Risk but based on the Atoti Market Data API:
- CorrelationMarketData
- DividendMarketData
- SplitRatioMarketData
If you have custom post-processors that retrieve data from these stores, refer to the Atoti Market Data documentation for the DirectQuery Local Cache.
note
As described in that documentation, the IDatabaseCacheManager is injected into Atoti Market Data post-processors by the com.activeviam.marketdata.config.directquery.DatabaseCacheManagerInjectionConfig configuration class.
Ensure this is imported in your project.
If you are using the out-of-the-box Atoti Market Risk project, it is imported in
AtotiMarketDataDirectQueryCacheConfig, which is itself imported by MarketRiskConfig.
Market Shift cache
If your post-processor queries the MarketShifts store, it should implement the IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor interface and implement the methods
as follows:
@AtotiExtendedPluginValue(intf = IPostProcessor.class, key = CustomMarketShiftPostProcessor.PLUGIN_KEY)
public class CustomMarketShiftPostProcessor extends ABasicPostProcessor implements IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor {
public static final String PLUGIN_KEY = "CustomMarketShiftPostProcessor";
@Getter @Setter private IDatabaseCacheManager databaseCacheManager;
@Getter @Setter private CacheConfiguration marketShiftCacheConfiguration;
public CustomMarketShiftPostProcessor(String name, IPostProcessorCreationContext creationContext) {
super(name, creationContext);
}
@Override
public List<IPrefetcher<?>> initializePrefetchers(Properties properties) {
var superPrefetchers = super.initializePrefetchers(properties);
return addDatabaseCachePrefetcher(superPrefetchers, properties, getActivePivot());
}
@Override
public void evaluate(ILocation location, IRecordReader recordReader, IWritableCell writableCell) {
// complete as required, including any get-by-key, distinct, or list queries that will read from the cache.
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return PLUGIN_KEY;
}
}
The market shifts cache configuration will be injected into the marketShiftCacheConfiguration property and the
IDatabaseCacheManager will be injected to the databaseCacheManager property. Calling the addDatabaseCachePrefetcher creates
a DatabaseCachePrefetcher using the cache configuration.
With this simple setup, your post-processor will populate the MarketShifts cache during the prefetch phase of a query.
note
This post-processor can be used in either a DirectQuery or an in-memory application, without any changes. If you are not running in DirectQuery mode, the
IDatabaseCacheManager is neither created nor injected into your post-processors. Without a cache manager the prefetcher is not created.
Caching new stores
If you add a new store and want to implement caching for it, you must provide a cache description for the store.
Expose your cache description as a bean:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryDatabase
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryCacheEnabled
public class CustomSideStoreCacheConfig {
// Provide a custom cache description for the custom side store
@Bean
public SingleTableCacheDescription customSideStoreCacheDescription() {
return SingleTableCacheDescription.builder()
.tableName(CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME)
.cachePartitioningFields(List.of(AS_OF_DATE))
.capacity(CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(6))
.build();
}
}
The DirectQueryActivePivotConfig class in the mr-directquery module collects these cache description beans and feeds them into the application configuration.
Make sure this class is imported in your project for the cache to work. This class is imported by MRDirectQueryConfig which is itself imported by
MarketRiskConfig in the mr-application module.
Additionally, your post-processors must configure an appropriate DatabaseCachePrefetcher.
Atoti Market Risk provides the IMRDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor to make this slightly easier. Post-processors implementing this interface will be injected with the
IDatabaseCacheManager that is required when creating the prefetcher (providing you include the injection configuration in your project).
There is also a helper method to make it easier to create the prefetcher:
Update your post-processor:
@AtotiExtendedPluginValue(intf = IPostProcessor.class, key = CustomPostProcessor.PLUGIN_KEY)
public class CustomPostProcessor extends ABasicPostProcessor implements IMRDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor {
public static final String PLUGIN_KEY = "CustomPostProcessor";
@Setter @Getter private IDatabaseCacheManager databaseCacheManager;
public CustomPostProcessor(String name, IPostProcessorCreationContext creationContext) {
super(name, creationContext);
}
@Override
public void init(Properties properties) throws ActiveViamException {
super.init(properties);
}
@Override
public String getCacheName(Properties properties) {
return CUSTOM_STANDALONE_STORE_NAME;
}
@Override
public ILocationToCachePartitionConverter getConverter(Properties properties) {
return new BestEffortLocationToCachePartitionConverter(List.of(
new LevelIdentifier(DATES_DIMENSION, DATE_HIERARCHY, AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL)));
}
@Override
public List<IPrefetcher<?>> initializePrefetchers(Properties properties) {
var superPrefetchers = super.initializePrefetchers(properties);
return addDatabaseCachePrefetcher(superPrefetchers, properties, getActivePivot());
}
@Override
public void evaluate(ILocation location, IRecordReader aggregatedMeasures, IWritableCell resultCell) {
// complete as required, including any get-by-key, distinct, or list queries that will read from the cache.
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return PLUGIN_KEY;
}
}
Worked example
This worked example contains two use cases:
Custom side store and custom post-processor
Let’s consider the following use-case:
- A custom side store needs to be added to the application.
- A custom post-processor that looks up entries in that side store needs to use DirectQuery caching for those retrievals.
The custom store will contain the fields:
AsOfDate(LocalDate) - key fieldInstrumentId(String) - key fieldQuote(Double)
The custom post-processor will do the following:
- Check if the queried location is at the as-of date and risk factor level.
- If yes, get the as-of date and the risk factor from the location.
- Retrieve the quote from the custom store using (as of date, risk factor) as the look-up key.
- Return the retrieved quote.
Here are the steps:
- Step 1: Configuration of custom store
- Step 2: The cache
- Step 3: The post-processor
- Step 4: The measure configuration
Step 1: Configuration of custom store
We will create the custom store definition as a @Configuration class in the package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.store.
To define a custom store, the class AConfigurableSchema can be extended; see the Datastore Helper section.
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.store;
import static com.activeviam.database.api.types.ILiteralType.DOUBLE;
import static com.activeviam.database.api.types.ILiteralType.LOCAL_DATE;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.constants.StoreFieldConstants.AS_OF_DATE;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.constants.StoreFieldConstants.INSTRUMENT_ID;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.constants.StoreFieldConstants.QUOTE;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.activeviam.database.datastore.api.description.IStoreDescription;
import com.activeviam.database.datastore.api.description.impl.DuplicateKeyHandlers;
import com.activeviam.tools.datastore.impl.AConfigurableSchema;
@Configuration
public class CustomSideStoreConfig extends AConfigurableSchema {
public static final String CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME = "CustomSide";
@Override
public void createStores() {
configurator.addStore(customSideStoreDescription(GLOBAL));
}
public IStoreDescription customSideStoreDescription(String schema) {
return configurator.storeBuilder(schema)
.withStoreName(CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME)
.withField(AS_OF_DATE, LOCAL_DATE, LocalDate.MIN).asKeyField()
.withField(INSTRUMENT_ID).asKeyField()
.withField(QUOTE, DOUBLE, 0.0)
.withDuplicateKeyHandler(DuplicateKeyHandlers.LOG_WITHIN_TRANSACTION)
.updateOnlyIfDifferent()
.build();
}
}
We also need to import the configuration class that we have just created in the MarketRiskConfig class:
@Import(value = {
...
// Added after all the other imports
CustomSideStoreConfig.class
})
public class MarketRiskConfig {
...
}
Step 2: The cache
To define the cache, we must specify the following:
- The side store for which the caching is used (it will be the custom store we have just defined).
- The partitioning fields (here we will use the
AsOfDatefield). - The capacity of the cache (we will set it to six partitions here as an example).
We will create the cache description as a @Configuration class in the package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.cache:
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.cache;
import static com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.store.CustomSideStoreConfig.CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.constants.StoreFieldConstants.AS_OF_DATE;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.activeviam.accelerator.common.spring.annotations.ConditionalOnDirectQueryDatabase;
import com.activeviam.directquery.api.cache.CacheCapacity;
import com.activeviam.directquery.api.cache.SingleTableCacheDescription;
import com.activeviam.mr.common.config.spring.annotations.ConditionalOnDirectQueryCacheEnabled;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryDatabase
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryCacheEnabled
public class CustomSideStoreCacheConfig {
// Provide a custom cache description for the custom side store
@Bean
public SingleTableCacheDescription customSideStoreCacheDescription() {
return SingleTableCacheDescription.builder()
.tableName(CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME)
.cachePartitioningFields(List.of(AS_OF_DATE))
.capacity(CacheCapacity.MaxPartitionsCount.of(6))
.build();
}
}
Here we use two annotations defined in the solution:
@ConditionalOnDirectQueryDatabase: This annotation is conditional on DirectQuery being enabled.@ConditionalOnDirectQueryCacheEnabled: This annotation is conditional on the DirectQuery cache being enabled.
These two annotations are needed so that the cache is only defined if both DirectQuery and the DirectQuery cache feature are enabled; see DirectQuery annotations.
We also need to import the configuration class that we’ve just created in the MarketRiskConfig class:
@Import(value = {
...
// Added after all the other imports
CustomSideStoreConfig.class,
CustomSideStoreCacheConfig.class
})
@Slf4j
public class MarketRiskConfig {
...
}
Step 3: The post-processor
note
This post-processor example focuses on the implementation and use of the DirectQuery cache. For production code, you may want to put the logic for the retrieval of the quote from the side store into its own service.
The post-processor will be created in the com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.postprocessor package.
We want to look-up data in the custom side store that we have defined for the location at which the post-processor is invoked.
To achieve that, we will extend the abstract class ABasicPostProcessor.
We also want to use the DirectQuery caching mechanism, so we will implement the IMRDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor interface; see Caching new stores.
To implement this interface, we will need the following:
- Getter and setter methods for the
IDatabaseCacheManagerobject. As a consequence of that, we need anIDatabaseCacheManagerattribute in the post-processor. - A
getCacheNamemethod that returns the name of the cache. - The implementation of the
ILocationToCachePartitionConverterinterface. - The implementation of the
initializePrefetchersmethod.
Let’s have a look at each of these points:
- The database cache manager object is added as an attribute and Lombok annotations are used for the getter and setter methods:
// The database cache manager
@Setter @Getter private IDatabaseCacheManager databaseCacheManager;
- The cache name that we use here is the same as the name of the custom side store.
Technically, the cache name is defined in the
SingleTableCacheDefinitionobject. We use the store name, but it’s not required.
@Override
public String getCacheName(Properties properties) {
// We will use the name of the custom side store as the name of the cache.
return CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME;
}
- The
ILocationToCachePartitionConverterthat we will use is theBestEffortLocationToCachePartitionConverterthat needs to take the as-of date level as parameter to match the as-of date field in the custom store:
@Override
public ILocationToCachePartitionConverter getConverter(Properties properties) {
// We will use the as-of date level for the cache
return new BestEffortLocationToCachePartitionConverter(List.of(
new LevelIdentifier(DATES_DIMENSION, DATE_HIERARCHY, AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL)));
}
- The
initializePrefetchersmethod retrieves the prefetchers already defined and adds the one we need for the DirectQuery cache:
@Override
public List<IPrefetcher<?>> initializePrefetchers(Properties properties) {
var superPrefetchers = super.initializePrefetchers(properties);
return addDatabaseCachePrefetcher(superPrefetchers, properties, getActivePivot());
}
In the evaluate method of the post-processor, we will:
- Check if the current location is at the as-of date and risk factor level. If it’s not, write a null result.
- If we’re at the as-of date and risk factor level, retrieve the members corresponding to these two levels in the location.
- The quote is retrieved from the side store with a get-by-key query. To optimize the query time, that get-by-key query is compiled
into a
IPreparedGetByKeyQuery. We check if the get-by-key query used to retrieve quotes in the custom standalone store has already been compiled. If not, we compile it. - Retrieve the quote in the custom standalone store with the key (as-of date, risk factor).
- If the retrieved quote isn’t null, write it to the current location, otherwise write a null result.
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.postprocessor;
import static com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.store.CustomSideStoreConfig.CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.constants.StoreFieldConstants.QUOTE;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.DATES_DIMENSION;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.DATE_HIERARCHY;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_DIMENSION;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_FACTORS_HIERARCHY;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.ext.api.postprocessing.directquery.BestEffortLocationToCachePartitionConverter;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.ext.api.postprocessing.directquery.ILocationToCachePartitionConverter;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.ext.api.postprocessing.fwk.ABasicPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.impl.api.cube.hierarchy.HierarchiesUtil;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.impl.api.location.LocationUtil;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.cube.metadata.ILevelInfo;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.cube.metadata.LevelIdentifier;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.location.ILocation;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.postprocessing.IPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.postprocessing.IPostProcessorCreationContext;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.postprocessing.IPrefetcher;
import com.activeviam.database.api.query.IPreparedGetByKeyQuery;
import com.activeviam.directquery.api.cache.IDatabaseCacheManager;
import com.activeviam.mr.common.services.IMRDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.tech.core.api.cell.IWritableCell;
import com.activeviam.tech.core.api.exceptions.ActiveViamException;
import com.activeviam.tech.core.api.registry.AtotiExtendedPluginValue;
import com.activeviam.tech.records.api.IRecordReader;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@AtotiExtendedPluginValue(intf = IPostProcessor.class, key = CustomSideStoreLookUpPostProcessor.PLUGIN_KEY)
public class CustomSideStoreLookUpPostProcessor extends ABasicPostProcessor implements IMRDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor {
// The post-processor plugin key
public static final String PLUGIN_KEY = "CustomSideStoreLookUpPostProcessor";
// The database cache manager
@Setter @Getter private IDatabaseCacheManager databaseCacheManager;
// ILevelInfo objects used to check if a location is at the as-of date and risk factor level.
// As-of date level info.
private ILevelInfo asOfDateLevelInfo;
// Risk factor level info.
private ILevelInfo riskFactorLevelInfo;
// The compiled get-by-key query used to retrieve the quote from the custom side store.
private IPreparedGetByKeyQuery compiledQuery;
public CustomSideStoreLookUpPostProcessor(String name, IPostProcessorCreationContext creationContext) {
super(name, creationContext);
}
@Override
public void init(Properties properties) throws ActiveViamException {
super.init(properties);
// Define the as-of date level info.
asOfDateLevelInfo = HierarchiesUtil.getLevel(getActivePivot(),
new LevelIdentifier(DATES_DIMENSION, DATE_HIERARCHY, AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL));
// Define the risk factor level info.
riskFactorLevelInfo = HierarchiesUtil.getLevel(getActivePivot(),
new LevelIdentifier(RISK_DIMENSION, RISK_FACTORS_HIERARCHY, RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL));
}
@Override
public String getCacheName(Properties properties) {
// We will use the name of the custom side store as the name of the cache.
return CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME;
}
@Override
public ILocationToCachePartitionConverter getConverter(Properties properties) {
// We will use the as-of date level for the cache
return new BestEffortLocationToCachePartitionConverter(List.of(
new LevelIdentifier(DATES_DIMENSION, DATE_HIERARCHY, AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL)));
}
@Override
public List<IPrefetcher<?>> initializePrefetchers(Properties properties) {
var superPrefetchers = super.initializePrefetchers(properties);
return addDatabaseCachePrefetcher(superPrefetchers, properties, getActivePivot());
}
// This method compiles the get-by key query used to retrieve quotes in the custom standalone store to speed up
// store look-ups
private IPreparedGetByKeyQuery preparedGetByKeyQuery() {
return getDatabaseVersion()
.getQueryManager()
.getByKeyQuery()
.forTable(CUSTOM_SIDE_STORE_NAME)
.withTableFields(QUOTE)
.compile();
}
@Override
public void evaluate(ILocation location, IRecordReader aggregatedMeasures, IWritableCell resultCell) {
// 1. Check if the current location is at the as-of date and risk factor level. If it is not, write a null result.
if (!LocationUtil.isAtOrBelowLevel(location, asOfDateLevelInfo) || !LocationUtil.isAtOrBelowLevel(location, riskFactorLevelInfo)) {
resultCell.writeNull();
return;
}
// 2. If we are at the as-of date and risk factor level, retrieve the members corresponding to those two levels in the location.
LocalDate asOfDate = (LocalDate) LocationUtil.getCoordinate(location, asOfDateLevelInfo);
String riskFactor = (String) LocationUtil.getCoordinate(location, riskFactorLevelInfo);
// 3. Check if the get-by-key query used to retrieve quotes in the custom standalone store has already been compiled.
// If it has not, compile it
if (compiledQuery == null) {
compiledQuery = preparedGetByKeyQuery();
}
// 4. Retrieve the quote in the custom standalone store with the key (as-of date, risk factor)
var recordReader = getDatabaseVersion()
.getQueryRunner()
.getByKeyQuery(compiledQuery)
.withKey(new Object[] { asOfDate, riskFactor })
.run();
// 5. If the retrieved quote is not null, write it to the current location, otherwise write a null result.
resultCell.write(recordReader != null ? recordReader.readDouble(0) : null);
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return PLUGIN_KEY;
}
}
Step 4: The measure configuration
We define a custom measure to use our post-processor in the package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.measure.
We use the annotation @SensitivitiesCopperContextBean to achieve that.
We simply create a post-processed measure with Copper using the plugin key of the post-processor and assigning a name to the measure:
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.measure;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.copper.api.Copper;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.copper.api.CopperMeasure;
import com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.postprocessor.CustomSideStoreLookUpPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.mr.sensi.measures.spring.intf.SensitivitiesCopperContextBean;
@Configuration
public class CustomSideStoreLookUpMeasureConfig {
@SensitivitiesCopperContextBean
@Qualifier("customSideStoreLookUpMeasure")
public CopperMeasure customSideStoreLookUpMeasure() {
return Copper.newPostProcessor(CustomSideStoreLookUpPostProcessor.PLUGIN_KEY).withFormatter("DOUBLE[#,##0.00;-#,##0.00]").as("Custom measure");
}
}
We need to import the configuration class that we’ve just created in the MarketRiskConfig class:
@Import(value = {
...
// Added after all the other imports
CustomSideStoreConfig.class,
CustomSideStoreCacheConfig.class,
CustomSideStoreLookUpMeasureConfig.class
})
@Slf4j
public class MarketRiskConfig {
...
}
Populating some data in the database
Here we take the example of a Databricks database in which we want to create our custom table and populate some sample data in it. We use the following SQL script:
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE CUSTOM_SIDE(
AS_OF_DATE DATE NOT NULL,
INSTRUMENT_ID STRING NOT NULL,
QUOTE DOUBLE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (AS_OF_DATE, INSTRUMENT_ID)
);
INSERT INTO CUSTOM_SIDE (AS_OF_DATE, INSTRUMENT_ID, QUOTE)
VALUES
('2018-09-28', 'AB Volvo_Spot price', 100.0),
('2018-09-28', 'Apple_Spot price', 200.0),
('2018-09-28', 'BMW_Spot price', 300.0);
How you populate your database may depend on your project’s requirements, so the steps to create and fill the custom table could differ from those in this example.
Testing the custom measure
The implementation is complete, we’re now going to see how that measure can be displayed.
By default, the DirectQuery cache feature is disabled. We need to enable it by using the property:
mr.enable.preview.directquery-cache=true.
We will also use the databricks Spring profile here to connect to a Databricks database, so that we can use the properties file
application-databricks.yaml.
We also need to use the CubeFeedingPromise.waitForAllSchemaAttachDatabase method that waits for all ActivePivot’s schema instances of the ActivePivot manager
to be attached to their parent database, otherwise the data from the database might not be loaded when the queries are run in the test.
We use the following integration test for our new measure:
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.integration;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.impl.api.cube.CubeFeedingPromise;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.cube.IActivePivotManager;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.server.spring.api.config.IActivePivotConfig;
import com.activeviam.atoti.server.test.api.CubeTester;
import com.activeviam.io.dlc.impl.annotations.ConditionalOnDlcEnabled;
import com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.config.ExamplesDQCacheConfig;
import com.activeviam.mr.application.main.MarketRiskApplication;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT, classes = {
MarketRiskApplication.class, ExamplesDQCacheConfig.class})
@TestPropertySource(properties = {
"mr.enable.preview.directquery-cache=true",
ConditionalOnDlcEnabled.DLC_ENABLED_PROPERTY + "=false"
})
@ActiveProfiles(profiles = { "local-content", "databricks" })
public class CustomSideStoreCachingTest {
@Autowired
IActivePivotManager manager;
@Autowired
IActivePivotConfig apConfig;
@Test
void testCustomSideStoreLookUpQuery() {
CubeFeedingPromise.waitForAllSchemaAttachDatabase(apConfig.activePivotManager());
CubeTester tester = CubeTester.from(manager);
var testResult = tester.mdxQuery().withMdx(
"""
SELECT
NON EMPTY {
[Measures].[Custom measure]
} ON COLUMNS,
NON EMPTY Hierarchize(
Descendants(
{
[Risk].[Risk Factors].[ALL].[AllMember]
},
1,
SELF_AND_BEFORE
)
) ON ROWS
FROM [Sensitivity Cube]
CELL PROPERTIES VALUE, FORMATTED_VALUE, BACK_COLOR, FORE_COLOR, FONT_FLAGS
""").run().show().getTester();
assertEquals(3, testResult.getCellsCount());
assertEquals(100.0, testResult.findCell().coordinate(RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL, "AB Volvo_Spot price").getCell().getValue());
assertEquals(200.0, testResult.findCell().coordinate(RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL, "Apple_Spot price").getCell().getValue());
assertEquals(300.0, testResult.findCell().coordinate(RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL, "BMW_Spot price").getCell().getValue());
}
}
Custom post-processor retrieving market shifts
Let’s consider the use-case of a custom post-processor that looks up entries in the existing MarketShifts store, using DirectQuery caching for those retrievals.
The custom post-processor will do the following:
- Check if the queried location is at the as-of date, scenario set and risk factor level.
- If yes, get the as-of date, the scenario set and the risk factor from the location.
- Retrieve the market shift vectors from the market shift store using (as of date, scenario set, risk factor) as the look-up key for a list query.
- Return the maximum of the retrieved market shifts.
Here are the steps:
- Step 1: The post-processor
- Step 2: The measure configuration
Step 1: The post-processor
note
This post-processor example focuses on the implementation and use of the DirectQuery cache. For production code, you may want to put the logic for the retrieval of the quote from the side store into its own service.
The post-processor will be created in the com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.postprocessor package.
We want to look up data in the market shift store for the location at which the post-processor is invoked.
To achieve that, we will extend the abstract class ABasicPostProcessor
We also want to use the DirectQuery caching mechanism, so we will also implement the IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor interface;
see Market Shift cache
To implement that interface, we will need:
- Getter and setter methods for the
IDatabaseCacheManagerobject. As a consequence of that, we need anIDatabaseCacheManagerattribute in the post-processor. - Getter and setter methods for the
CacheConfigurationobject defining the caching of market shifts. As a consequence of that, we need anCacheConfigurationattribute in the post-processor. The cache name and theILocationToCachePartitionConverterobject will be taken from theCacheConfigurationobject defined in that attribute. If a different cache name or a different converter are needed, the methodsgetCacheNameandgetConvertercan be overridden. - The implementation of the
initializePrefetchersmethod.
Let’s have a look at each of these points:
- The database cache manager object is added as an attribute and Lombok annotations are used for the getter and setter methods:
// The database cache manager
@Setter @Getter private IDatabaseCacheManager databaseCacheManager;
- The cache configuration object is added as an attribute and Lombok annotations are used for the getter and setter methods:
// The cache configuration for market shifts
@Setter @Getter private CacheConfiguration marketShiftCacheConfiguration;
- The
initializePrefetchersmethod retrieves the prefetchers already defined and adds the one we need for the DirectQuery cache:
@Override
public List<IPrefetcher<?>> initializePrefetchers(Properties properties) {
var superPrefetchers = super.initializePrefetchers(properties);
return addDatabaseCachePrefetcher(superPrefetchers, properties, getActivePivot());
}
In the evaluate method of the post-processor, we will:
- Check if the current location is at the as-of date, scenario set, and risk factor level. If it is not, write a null result.
- If we are at the as-of date, scenario set and risk factor level, retrieve the members corresponding to those three levels in the location.
- The shift vectors are retrieved from the market shift store with a list query. To optimize the query time, that list query is compiled
into an
IPreparedGetByKeyQuery. We check if the list query has already been compiled. If not, we compile it. - Retrieve the shift vectors in the market shift store with the key (as-of date, scenario set, risk factor).
- Loop over the retrieved vectors to compute the maximum of the shifts.
- Write the computed maximum to the current location.
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.postprocessor;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.DATES_DIMENSION;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.DATE_HIERARCHY;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_DIMENSION;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_FACTORS_HIERARCHY;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.SCENARIO_SET_HIERARCHY;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.cube.dimensions.DimensionConstantsConfig.SCENARIO_SET_LEVEL;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.datastore.description.stores.MarketShiftStoreConfig.MARKET_SHIFT_SENSITIVITY_VALUES;
import static com.activeviam.mr.common.datastore.description.stores.MarketShiftStoreConfig.MARKET_SHIFT_STORE_NAME;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.ext.api.postprocessing.fwk.ABasicPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.impl.api.cube.hierarchy.HierarchiesUtil;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.impl.api.location.LocationUtil;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.cube.metadata.ILevelInfo;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.cube.metadata.LevelIdentifier;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.location.ILocation;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.postprocessing.IPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.postprocessing.IPostProcessorCreationContext;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.core.intf.api.postprocessing.IPrefetcher;
import com.activeviam.database.api.ICondition;
import com.activeviam.database.api.conditions.BaseConditions;
import com.activeviam.database.api.query.IPreparedListQuery;
import com.activeviam.database.api.schema.FieldPath;
import com.activeviam.directquery.api.cache.IDatabaseCacheManager;
import com.activeviam.mr.common.constants.StoreFieldConstants;
import com.activeviam.mr.common.services.IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.tech.core.api.cell.IWritableCell;
import com.activeviam.tech.core.api.exceptions.ActiveViamException;
import com.activeviam.tech.core.api.registry.AtotiExtendedPluginValue;
import com.activeviam.tech.records.api.ICursor;
import com.activeviam.tech.records.api.IRecordReader;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@AtotiExtendedPluginValue(intf = IPostProcessor.class, key = CustomMarketShiftLookUpPostProcessor.PLUGIN_KEY)
public class CustomMarketShiftLookUpPostProcessor extends ABasicPostProcessor implements IMarketShiftDirectQueryCachingPostProcessor {
// The post-processor plugin key
public static final String PLUGIN_KEY = "CustomMarketShiftsPostProcessor";
// The database cache manager
@Setter @Getter private IDatabaseCacheManager databaseCacheManager;
// The cache configuration for market shifts
@Setter @Getter private CacheConfiguration marketShiftCacheConfiguration;
// ILevelInfo objects used to check if a location is at the as-of date and risk factor level.
// As-of date level info.
private ILevelInfo asOfDateLevelInfo;
// Risk factor level info.
private ILevelInfo riskFactorLevelInfo;
// Scenario Set level info.
private ILevelInfo scenarioSetLevelInfo;
// The compiled get-by-key query used to retrieve the quote from the custom side store.
private IPreparedListQuery compiledQuery;
private static final ICondition MARKET_SHIFT_CONDITION = BaseConditions.and(
BaseConditions.equal(FieldPath.of(StoreFieldConstants.AS_OF_DATE)).as(StoreFieldConstants.AS_OF_DATE),
BaseConditions.equal(FieldPath.of(StoreFieldConstants.RISK_FACTOR_ID)).as(StoreFieldConstants.RISK_FACTOR_ID),
BaseConditions.equal(FieldPath.of(StoreFieldConstants.SCENARIO_SET)).as(StoreFieldConstants.SCENARIO_SET));
public CustomMarketShiftLookUpPostProcessor(String name, IPostProcessorCreationContext creationContext) {
super(name, creationContext);
}
@Override
public void init(Properties properties) throws ActiveViamException {
super.init(properties);
// Define the as-of date level info.
asOfDateLevelInfo = HierarchiesUtil.getLevel(getActivePivot(),
new LevelIdentifier(DATES_DIMENSION, DATE_HIERARCHY, AS_OF_DATE_LEVEL));
// Define the risk factor level info.
riskFactorLevelInfo = HierarchiesUtil.getLevel(getActivePivot(),
new LevelIdentifier(RISK_DIMENSION, RISK_FACTORS_HIERARCHY, RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL));
// Define the scenario set level info.
scenarioSetLevelInfo = HierarchiesUtil.getLevel(getActivePivot(),
new LevelIdentifier(RISK_DIMENSION, SCENARIO_SET_HIERARCHY, SCENARIO_SET_LEVEL));
}
@Override
public List<IPrefetcher<?>> initializePrefetchers(Properties properties) {
var superPrefetchers = super.initializePrefetchers(properties);
return addDatabaseCachePrefetcher(superPrefetchers, properties, getActivePivot());
}
// This method compiles the get-by key query used to retrieve quotes in the custom standalone store to speed up
// store look-ups
private IPreparedListQuery preparedListQuery() {
return getDatabaseVersion()
.getQueryManager()
.listQuery()
.forTable(MARKET_SHIFT_STORE_NAME)
.withCondition(MARKET_SHIFT_CONDITION)
.withTableFields(MARKET_SHIFT_SENSITIVITY_VALUES)
.compile();
}
@Override
public void evaluate(ILocation location, IRecordReader aggregatedMeasures, IWritableCell resultCell) {
//1. Check if the current location is at the as-of date, scenario set, and risk factor level. If it is not, write a null result.
if (!LocationUtil.isAtOrBelowLevel(location, asOfDateLevelInfo) || !LocationUtil.isAtOrBelowLevel(location, riskFactorLevelInfo)
|| !LocationUtil.isAtOrBelowLevel(location, scenarioSetLevelInfo)) {
resultCell.writeNull();
return;
}
// If we are at the as-of date, scenario set and risk factor level, retrieve the members corresponding to those three levels in the location.
LocalDate asOfDate = (LocalDate) LocationUtil.getCoordinate(location, asOfDateLevelInfo);
String riskFactor = (String) LocationUtil.getCoordinate(location, riskFactorLevelInfo);
String scenarioSet = (String) LocationUtil.getCoordinate(location, scenarioSetLevelInfo);
// 3. Check if the list query used to retrieve shift vectors in the market shift store has already been compiled.
// If it has not, compile it
if (compiledQuery == null) {
compiledQuery = preparedListQuery();
}
// 4. Retrieve the shift vectors in the market shift store with the key (as-of date, scenario set, risk factor).
Double maxShift = null;
try (ICursor cursor = getDatabaseVersion()
.getQueryRunner()
.listQuery(compiledQuery)
.withParameters(Map.of(
StoreFieldConstants.AS_OF_DATE, asOfDate,
StoreFieldConstants.RISK_FACTOR_ID, riskFactor,
StoreFieldConstants.SCENARIO_SET, scenarioSet))
.runCurrentThread()) {
// 5. Loop over the retrieved vectors to compute the maximum of the shifts.
for (IRecordReader recordReader : cursor) {
double maxForCurrentRecord = recordReader.readVector(0).bottomK(1).nextDouble();
maxShift = maxShift == null ? maxForCurrentRecord : Math.max(maxShift, maxForCurrentRecord);
}
}
// 6. Write the computed maximum to the current location
resultCell.write(maxShift);
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return PLUGIN_KEY;
}
}
Step 2: The measure configuration
We will define a custom measure to use our post-processor in the package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.measure.
We will use the annotation @SensitivitiesCopperContextBean to achieve that.
We simply create a post-processed measure with Copper, using the plugin key of the post-processor and assigning a name to the measure:
package com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.measure;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.copper.api.Copper;
import com.activeviam.activepivot.copper.api.CopperMeasure;
import com.activeviam.mr.application.examples.dqcache.postprocessor.CustomMarketShiftLookUpPostProcessor;
import com.activeviam.mr.sensi.measures.spring.intf.SensitivitiesCopperContextBean;
@Configuration
public class CustomMeasureMarketShiftsConfig {
@SensitivitiesCopperContextBean
@Qualifier("customMarketShiftLookUpMeasure")
public CopperMeasure customMarketShiftLookUpMeasure() {
return Copper.newPostProcessor(CustomMarketShiftLookUpPostProcessor.PLUGIN_KEY).withFormatter("DOUBLE[#,##0.0000;-#,##0.0000]").as("Custom Market Shift measure");
}
}
We need to import the configuration class that we have just created in the MarketRiskConfig class:
@Import(value = {
...
// Added after all the other imports
CustomSideStoreConfig.class,
CustomSideStoreCacheConfig.class,
CustomSideStoreLookUpMeasureConfig.class,
CustomMeasureMarketShiftsConfig.class
})
@Slf4j
public class MarketRiskConfig {
...
}
Testing the custom measure
The implementation is complete, we’re now going to see how that measure can be displayed. We will update the integration test that we created earlier with a new method:
@Test
void testCustomMarketShiftLookUpQuery() {
CubeFeedingPromise.waitForAllSchemaAttachDatabase(apConfig.activePivotManager());
CubeTester tester = CubeTester.from(manager);
var testResult = tester.mdxQuery().withMdx(
"""
SELECT
NON EMPTY {
[Measures].[Custom Market Shift measure]
} ON COLUMNS,
NON EMPTY Hierarchize(
Descendants(
{
[Risk].[Risk Factors].[ALL].[AllMember]
},
1,
SELF_AND_BEFORE
)
) ON ROWS
FROM (
SELECT
{
[Risk].[Risk Factors].[ALL].[AllMember].[AB Volvo_Implied volatility],
[Risk].[Risk Factors].[ALL].[AllMember].[AB Volvo_Spot price],
[Risk].[Risk Factors].[ALL].[AllMember].[Allegheny Energy_Credit spread]
} ON COLUMNS
FROM [Sensitivity Cube]
)
CELL PROPERTIES VALUE, FORMATTED_VALUE, BACK_COLOR, FORE_COLOR, FONT_FLAGS
""").run().show().getTester();
assertEquals(3, testResult.getCellsCount());
assertEquals(-0.14143821059364572, testResult.findCell().coordinate(RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL, "AB Volvo_Implied volatility").getCell().getValue());
assertEquals(-16.923453485618467, testResult.findCell().coordinate(RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL, "AB Volvo_Spot price").getCell().getValue());
assertEquals(-6.973620821803489, testResult.findCell().coordinate(RISK_FACTOR_LEVEL, "Allegheny Energy_Credit spread").getCell().getValue());
}