Database API
An Atoti cube can work on top of a Datastore or an external data warehouse.
Therefore, a common interface is used to represent any component capable of providing versioned data for the cube.
This interface is com.activeviam.database.api.IDatabase.
This interface has two kind of implementations:
IDatastorewhich is the Atoti implementation of an in-memory database.IDirectQueryDatabasewhich is an implementation that supports querying an external data warehouse.
An Atoti cube can use any IDatabase as a data provider.
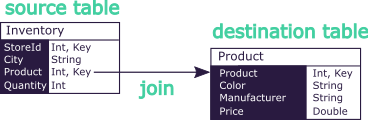
Database Schema
The database schema consists of a set of tables, each containing fields, and that are interlinked with joins.
For those used to the vocabulary historically used in the Datastore, the tables used to be called stores, and the joins used to be called references.
Naming joins is not something that exists in common databases.
In the context of Atoti where it is mandatory to pre-define a flattened schema, it is convenient to assign names to those paths.
This makes it easier reason about those fields as integrated to the schema.
Versions
Atoti Databases have the same concept of versions and branches that were previously exposed by the Datastore and Atoti cubes. As before, they represent single points in time of the Database and alternative scenarii on the dataset.
Query Runner
This component is accessed from a Version though the method IDatabaseVersion#getQueryRunner.
The Query Runner is the entry-point to run queries on a Database. It can run different types of queries:
- List: These queries are made to retrieve a list of records that match some specified conditions.
- Get-By-Key: These queries are made to retrieve one or several records (lines of data in a table) for which we know the unique identifier (e.g. the key).
- Statistics: These queries are made to retrieve information about the Database. Details like the size of a table, or the cardinality of a given field.
- Distinct: These queries are made to retrieve distinct values of a field or a field combination from a list of records. The list of records can be optionally filtered with specified conditions.
Query Manager
This component is accessed from a Version though the method IDatabaseVersion#getQueryManager or from the database itself.
Completing the Query Runner, the Query Manager makes it possible to prepare queries beforehand.
Using an analogy with JDBC, the Query Runner creates an SQL Statement while the Query Manager creates Prepared Statements.
In the language of the QueryManager, it produces instances of IPreparedQuery
The benefits of Prepared Queries include compiling-once, managing, parametrizing and reusing them.
Once created, those queries must be passed to a given Query Runner to be executed in a given version.
Data streamer
This component is accessed from the database though the method IDatabase#getDataStreamer.
You can register an IPreparedListQuery in the streamer. On data change, if it impacts the result of the query, the streamer transmits refresh operations to the listener.