JDBC Source
Introduction
A JDBCSource is a database-related implementation of the ISource interface. It is the generic
framework used in ActivePivot for fetching from external data sources and contributing in an
ActivePivot Datastore.
The purpose of the JDBCSource is to load data from a database, through a JDBC driver.
Parameters
A JDBCSource has several parameters:
Connection information
- Username/Password/Class of the JDBC Driver
OR
- Implementation of the
IConnectionSupplierfunctional interface, which wraps the connection information. ThecreateConnection()method of the connectionSupplier provides ajava.sql.Connectionand loads JDBC drivers according to the implementation.
Source Properties: these properties are either a field of the JDBC source or a property of one of its fields.
poolSize: input argument given to the Source Constructor that drives the size of the ThreadPool in which theJDBCTaskis executed (defaults to 2). It can be an impacting factor when trying to fetch data of the underlying topic from numerous channels at the same time.appendQueueSize: size of the append queue that receives the parsed records of a givenJDBCTask. This property should be set at a larger value thanbatchSizeandJDBCTopic#fetchSize, since those properties correspond to push/pop operations on a collection.batchSize: size of the collection aJDBCAppendRunnableperforms on the append queue.
Topic Properties: these properties are not directly linked to a JDBCSource, but impact source performance when asked to fetch topic-related data.
JDBCTopic#fetchSize: size used to receive SQL request answer. While fetching data from ajava.sql.ResultSet, we only fetch fetchSize-sized pieces of theResultSetat once, which can be useful for controlling network usage congestion. This property can be the performance bottleneck of the source.JDBCTopic#nbAppendThreads: size of the thread pool in which theJDBCAppendRunnableis executed.JDBCTopic#chunkSize: size of the data chunks sent to theChannelMessageto send on to the datastore.
While fetching data with a JDBCSource, ActivePivot monitors the size of the append queue.
If the queue reaches full capacity, it becomes the limiting factor for the data fetching operation.
In that case, one can increase the size of the thread-pool through JDBCTopic#nbAppendThreads, or
change the JDBCSource#batchSize value.
A JDBCSource connects to a given database by using the provided connection information.
Once the connection has been tested, data can be fetched from the database by calling the fetch([...]) method:
Map<String, IJdbcFetchingInfo> fetch(Map<IMessageChannel<String, T>, List<Object>> channelsAndParams);
A JDBCSource does not need a topic to be instantiated, but topics must be added to the source before any query execution. This is done with the addTopic([...]) method.
The fetch([...]) method retrieves all available data as defined by the topics exposed by the channels given in arguments. They can either be SQL queries or a Java.sql.PreparedStatement. Then it fills the corresponding channels with the parsed results.
The provided implementations of IJDBCSource extend AJDBCSource and mostly differ in the way the ResultSet obtained by executing the Query is parsed:
ArrayJDBCSourceparses the ResultSet asObject[]MapJDBCSourceparses the ResultSet asMap<String,Object>NativeJDBCSourceparses the ResultSet asQfsResultRow
Usage Example
Create the ArrayJDBCSource source using a IConnectionSupplier implementation, which attempts to use the H2 database driver:
final IJDBCSource<Object[]> source = IJDBCSource.builder()
.arrayRows()
.withConnectionInfo(url, username, password, driverClass)
.withName(sourceName)
.build();
Additional source properties can be modified for a more fine-tuned configuration.
Create the topic, here a preparedStatement, and add it to the source:
final JDBCTopic topic = new JDBCTopic(topicName, "SELECT DESK, BOOK, PNL FROM RECORDS WHERE DESK=?");
source.addTopic(topic);
Default Topic parameters are implied here, but can also be modified to tune the performances of the source.
An IMessageChannelFactory implementation creates the channels between the topics of the source and the stores of a datastore:
final JDBCMessageChannelFactory channelFactory = new JDBCMessageChannelFactory(source, datastore);
final IMessageChannel<String, QfsResultSetRow> channel =
channelFactory.createChannel(topicName, store.toString());
Specify the requested values in the topic, then execute the query and fill the channel:
source.fetch(channel, Arrays.asList("Desk A"));
Handling vectors
JDBC ARRAY type will be automatically converted to an IVector which underlying type depends on the type of the ARRAY in the database.
To pick a specific vector type, core column calculators can be used: DoubleArrayJdbcColumnCalculator, FloatArrayJdbcColumnCalculator, IntegerArrayJdbcColumnCalculator or LongArrayJdbcColumnCalculator.
For instance for double vectors:
channelFactory.setCalculatedColumns(
topicName,
storeName,
List.of(new DoubleArrayJdbcColumnCalculator("PNL_VECTOR")));
Fetching data
The fetch([...]) method performs most of the task of a JDBCSource: it executes queries on a database and puts the parsed data in channels that feed into a Datastore.
Also, if the PARSING_REPORT_ENABLED property is set to true, it returns a JDBCFetchingInfo object for each topic, which contains various statistics about the fetched data,
such as which columns it contains, how many lines were published to the datastore and how long this process took.
This is performed in parallel:
For each entry in the input map (for instance, a MessageChannel-Parameters pair), fetch([...]) creates a JDBCTask. Those are executed concurrently on a thread pool dimensioned by an input property of the source.
Here is a sequence diagram displaying the execution of the fetch([...]) method on multiple channels. JDBCTask and JDBCAppendRunnable are documented more thoroughly below.
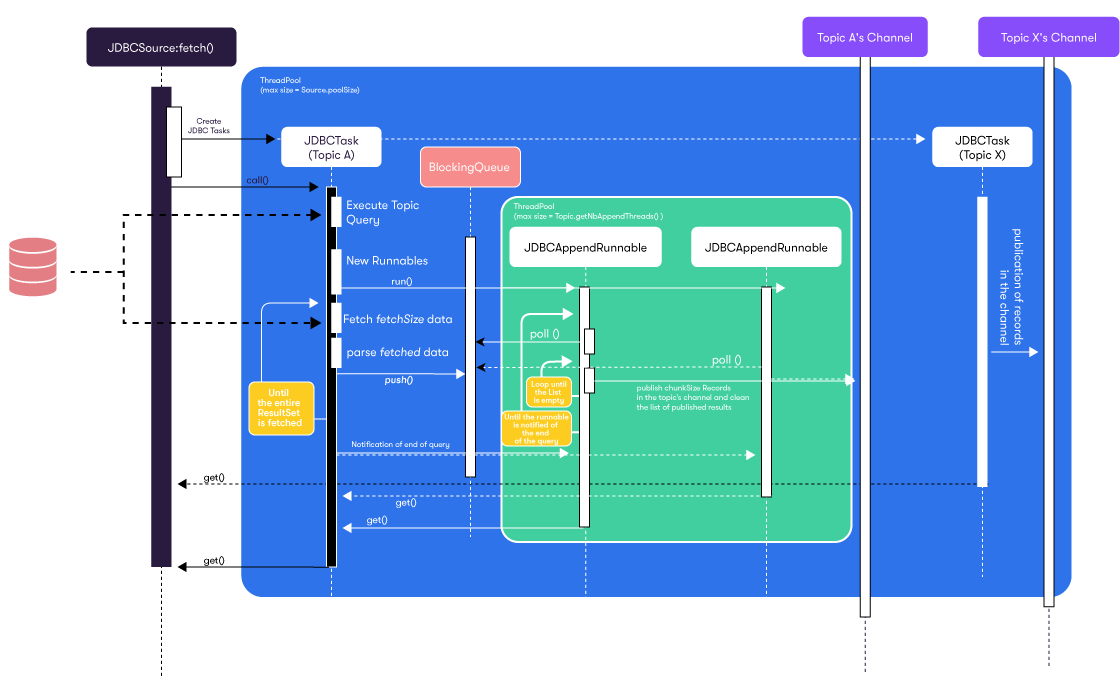
JDBCTask
Each JDBCTask performs the following tasks:
Executes the query on the database.
Launches and keeps track of concurrent
JDBCAppendRunnables on a thread pool dimensioned by a property of the topic related to theJDBCTask.Creates an append queue from which the runnables poll.
Fetches the corresponding
java.sql.ResultSet.To avoid network congestion, data from the
ResultSetis recovered by fetchSize-sized pieces.Iterates over the fetchSize-sized piece of the
ResultSetuntil the data is entirely recovered:- Parses the data as a collection of
Records by using theJDBCSource#createRecord()implementation of the current source. - Feeds it to the append queue.
- Parses the data as a collection of
When the ResultSet has been entirely processed, the JDBCAppendRunnables are notified, and we wait for the termination of all the linked threads to proceed and terminate the JDBCTask.
JDBCAppendRunnable
Each JDBCAppendRunnable performs the following tasks until the underlying JDBCTask sends notification that its append queue is empty and won't be filled anymore:
- Attempts to drain the queue by batchSize-sized pieces into a
List<Record>. - Pushes the records from the
Listinto the channel'sIMessageby chunkSize-sized pieces.
Monitoring JDBC Source
The JDBC Source contributes to the Health Event Monitoring, under the tags jdbc and source.
The following snippet adds the basic implementation of the listener to the handler stack.
HealthEventDispatcher.INSTANCE.addEventHandler(new LoggingJdbcHealthEventHandler());
This uses the default logger to report all JDBC operations. By default, there is no filtering on the received events.